

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Orbitals
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
13-8-2020
2020
Orbitals
We can apply our knowledge of quantum numbers to describe the arrangement of electrons for a given atom. We do this with something called electron configurations. They are effectively a map of the electrons for a given atom. We look at the four quantum numbers for a given electron and then assign that electron to a specific orbitals below.
s Orbitals For any value of n , a value of l=0 places that electron in an s orbital. This orbital is spherical in shape:
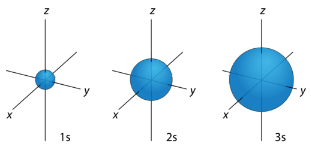
Figure 1: s orbitals have no orientational preference and resemble spheres.
p Orbitals For the table below, we see that we can have three possible orbitals when l=1 . These are designated as p orbitals and have dumbbell shapes. Each of the p
orbitals has a different orientation in three-dimensional space.
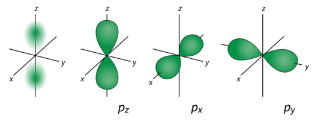
Figure 2 : p orbitals have an orientational preference and resemble dumbells. d Orbitals When l=2 , ml values can be −2,−1,0,+1,+2 for a total of five d orbitals. Note that all five of the orbitals have specific three-dimensional orientations.
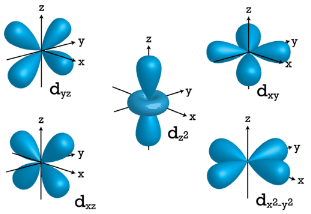
Figure 3 :d orbitals have an orientational preference and exhibit complex structures. f Orbitals The most complex set of orbitals are the f orbitals. When l=3, ml values can be −3,−2,−1,0,+1,+2,+3 for a total of seven different orbital shapes. Again, note the specific orientations of the different f
orbitals.

Figure 4 : f orbitals have an orientational preference and exhibit quite complex structures.
Orbitals that have the same value of the principal quantum number form a shell. Orbitals within a shell are divided into subshells that have the same value of the angular quantum number. Some of the allowed combinations of quantum numbers are compared in Table 1:
Table 1: Electron Arrangement Within Energy Levels
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء عامة
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء عامة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















