

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الحيوية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الحيوية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
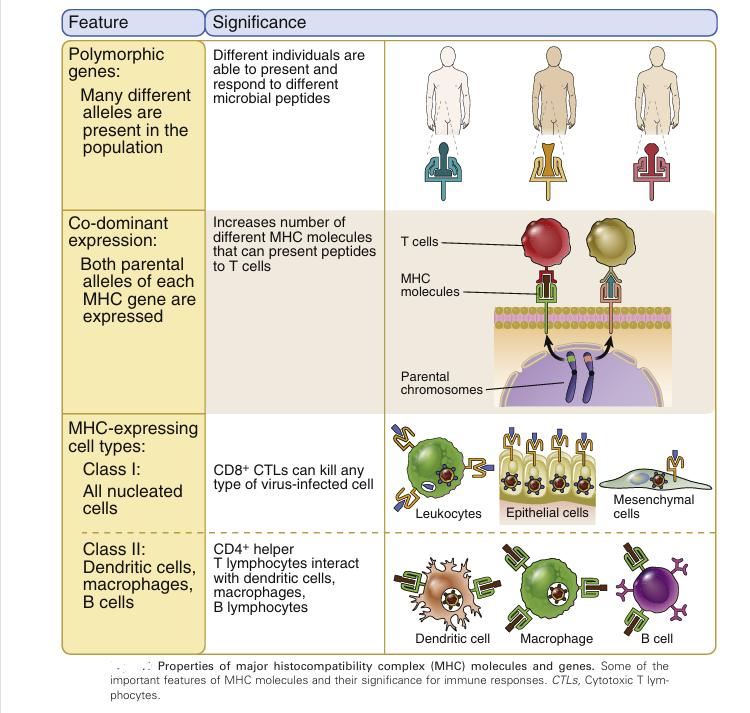
Properties of MHC Genes and Proteins
المؤلف:
Abbas, A. K., Lichtman, A. H., & Pillai, S
المصدر:
Basic Immunology : Function and disorders of immune system
الجزء والصفحة:
6th ed , page59-60
2025-01-05
940
Several features of MHC genes and proteins are important for the normal function of these molecules
- MHC genes are highly polymorphic, meaning that many different alleles (variants) are present among the different individuals in the population. The total number of different HLA proteins in the population is estimated to be more than 14,000, with about 10,500 class I and 3500 class II molecules, making MHC molecules the most polymorphic of all proteins in mammals. The polymorphism of MHC proteins is so great that any two individuals in an outbred population are extremely unlikely to have exactly the same MHC molecules. These different polymorphic variants are inherited and not generated de novo in individuals by somatic gene recombination, as are antigen receptors . Any one individual inherits and expresses only two alleles of each MHC gene (one from each parent), which represent very few of the many variants in the population. Because the polymorphic residues determine which peptides are presented by specific MHC molecules, the existence of multiple alleles ensures that there are always some members of the population who will be able to present some peptide from any particular microbial protein antigen. There- fore, MHC polymorphism ensures that a population will be able to deal with the diversity of microbes, and at least some individuals will be able to mount effective immune responses to the peptide antigens of these microbes. Thus, everyone will not succumb to a newly encountered or mutated microbe.
- MHC genes are codominantly expressed, meaning that the alleles inherited from both parents are expressed equally. Codominant expression maximizes the number of HLA proteins expressed by each individual and thus enables each individual to display a large number of peptides.
- Class I molecules are expressed on all nucleated cells, but class II molecules are expressed mainly on dendritic cells, macrophages, and B lymphocytes. The physiologic significance of this strikingly different expression pattern is described later. Class II molecules also are expressed on thymic epithelial cells and endothelial cells and can be induced on other cell types by the cytokine interferon-γ.
 الاكثر قراءة في المناعة
الاكثر قراءة في المناعة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















