

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


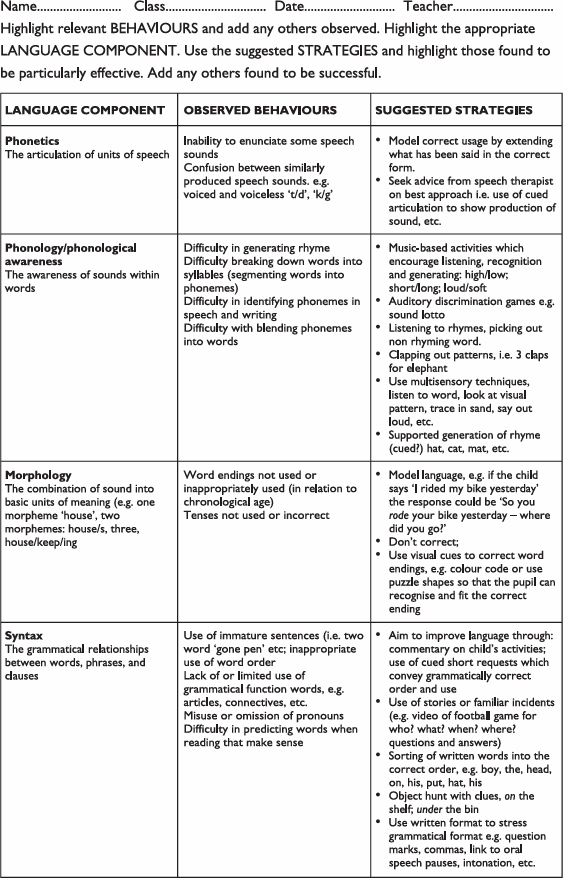
Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

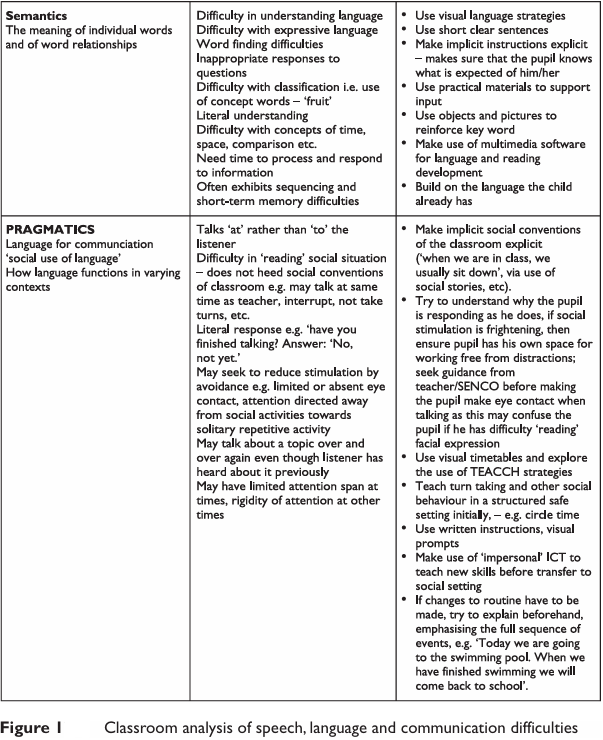
Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Attention and listening
المؤلف:
Janet Tod and Sue Soan
المصدر:
Additional Educational Needs
الجزء والصفحة:
P179-C12
2025-04-27
824
Attention and listening
A pupil is more likely to attend and listen if the following conditions are met:
■ He or she has some familiarity with the content and purpose of the lesson. TAs can fulfil a valuable role in ‘briefing’ the pupil before the lesson about vocabulary that will be used, etc. Homework set may be ‘in preparation’ for the next lesson so that the pupil has had time to familiarize her or himself with the content.
■ Distractions and noise are kept to a minimum.
■ He or she is ‘cued’ to listen either by the instruction ‘Listen, Jamie’ or by a cue card (containing the class symbol for listening)
■ Verbal or written instruction is supported by pictorial cues and use of gesture.
■ The content of the lesson is meaningful to the pupil and linked to familiar vocabulary.
■ Instructions are brief and explicit.
■ He or she is clear about what he or she has to listen for, e.g. not a whole story, but the names of animals in the story.
■ Intersperse short bouts of listening with doing – not both at once.
■ He or she is motivated but not overly anxious.
Pupils remember best when the following conditions are met:
■ The things that need to be remembered are of interest and value to them.
■ There is opportunity for re-processing the material in different formats: i.e. making flow diagrams; mind maps, mnenonics, re-telling the main points to a peer; making a poster of key points, etc.
■ Learning involves practical activities and social experiences.
■ There are opportunities for practice and regular use.
■ Explicit links are made to the individual’s existing knowledge and understanding.
 الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















