

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Overall results
المؤلف:
Stephen Gomez & Richard Osborne
المصدر:
Enhancing Teaching and Learning through Assessment
الجزء والصفحة:
P43-C5
2025-06-02
501
Overall results
When students were asked to reflect on the mark awarded compared to their expectations of the mark they felt they should have received, 40% students agreed that the mark was as they expected; 44% said it was lower than expected and just 16% felt that it had exceeded their expectations (Fig.1).
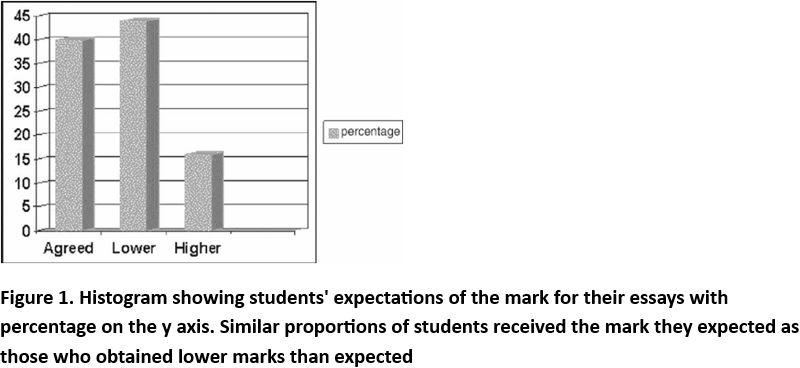
In the case of the feedback given, 50% of students reported their initial agreement with the comments made. However, following reflection, 88% of students noted that the feedback was accurate and had enhanced their understanding of what was required by the essay title as well as the subject matter under consideration.
Over 90% students said that the most useful comments made were those directing them towards using the "aetiology of Parkinson's Disease and late onset polio symptoms as models of a neurological time-bomb", "exploring the effect of ecstasy on dopamine as well as serotonin" and giving a detailed account of key synthetic enzymes. Only one student completely disagreed with the feedback noting that the "exercise was ridiculous at this level [i.e. final year of the degree]", the "assessor was biased" and that "I wished that I had read all the comments relating to this essay ASAP so that I could have made a complaint"!
Most of the subsequent student action plans noted the need to understand all the words and the meaning of the title overall. The majority of students noted that the key word in the title was "time-bomb" and reported that they had chosen to ignore it when compiling the original essay and consequently had missed the required emphasis. Others noted that as a result of this exercise they would "spend more time contemplating weaknesses in my writing", "be aware of when it is important to expand upon an idea", have a more open mind "when reading the background material", "would not rush into answering the question without considering other relevant views", "make points explicitly rather than just hinting at them".
Despite these encouraging comments, the students disliked having to perform a reflective assignment, considered it to be "inappropriate and unnecessary at final year level" as evidenced by responses given on an anonymous questionnaire. This attitude supports the work of Jackson (1995) who reported that level 3 students tended to only look at the grade rather than at the feedback. He also found that students like to see feedback to reassure them that their assignment has been marked fairly.
Although students agreed with the statement that they learned from feedback they were non-committal as to the value of having a reflective assignment. We found a higher level of learning occurring with the reflective assignment than with the essay component but this was not recognized by most students.
 الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















