

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Peer Assessment among Students in a Problem-Based Learning Format Conclusions
المؤلف:
Steve Frankland
المصدر:
Enhancing Teaching and Learning through Assessment
الجزء والصفحة:
P152-C14
2025-06-28
618
Peer Assessment among Students in a Problem-Based Learning Format Conclusions
The complete case study takes around six hours to complete and is used for two separate sessions of 3 hours per session. In total, about 180 postgraduate students in around 40 groups in five separate classes have participated over a period of five years. These have ranged from classes where the number of groups was four up to classes where the number of groups was 11.
In terms of strengths, the results have consistently found that students:
• consider it an interesting, relevant, and effective method of learning
• working on a realistic problem makes them see the relevance of their studies
• has the advantages of PBL, i.e. students learn better by "doing" and this promotes deep understanding rather than surface learning
• promotes group learning, i.e. students learn from each other, particularly postgraduate students
• have the opportunity to Peer Assess (and grade) each other's work, which they find both very interesting and a useful learning experience in its own right.
Students often expect a "model" or "correct" solution to a problem. What has been done in this case is to change this problem into an experience where they were made to recognize that there are seldom such solutions. In real engineering situations, student must deal with an accumulation of both technical and managerial facts wholistically.

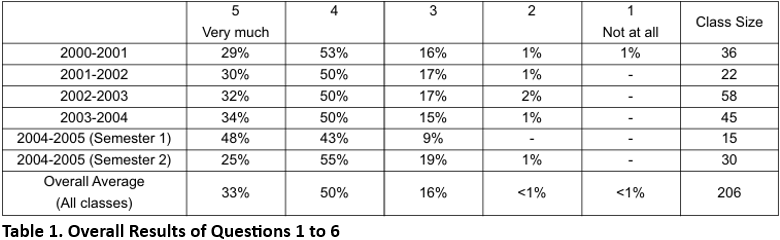
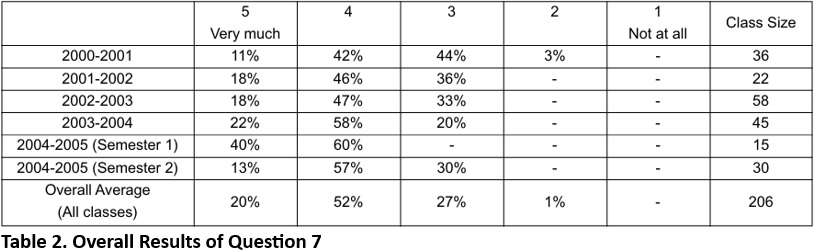
In terms of weaknesses:
• it's more work for the teacher, in preparation as well as execution, since it has to be well organized, especially with larger size classes - but it's worth it!
• it occupies considerable time - in this case it was 6 hours out of 42 hours class contact (around 14%), two topics were covered, namely: Layout Planning and Evaluation.
In summary, this case helps students to develop their thinking and decision making skills through practice on a real life scenario. They tend to do all of the thinking, originate their own ideas, learn from each other, organize the discussion, and establish priorities that covers the material in the time available without interference from the teacher. They learn by doing, promoting deep learning, rather learning by listening, which tends to promote surface learning. Moreover, they recognize that successful treatment of engineering situations often involves a compromise between both individual preference of group members depending on their way of looking at a situation and subjectivity of deciding upon a particular solution as only one of many possible solutions.
 الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















