

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
Enrichment of Interaction in Online Assessments Paul Lam & Paula Hodgson & Josephine Csete
المؤلف:
Paul Lam & Paula Hodgson & Josephine Csete
المصدر:
Enhancing Teaching and Learning through Assessment
الجزء والصفحة:
P392-C33
2025-08-09
392
Enrichment of Interaction in Online Assessments
Learning occurs when learners impart meanings and structures to knowledge and information (Taylor and Maor, 2000). Learning is thus thought to be enhanced by engaging students in an interactive learning environment, as feedback and reflection effectively help knowledge construction (O'Connor, 1998).
The engagement of learners in a learning environment of this kind is a key reason for bringing learning technologies into teaching (Baldwin et al., 2000). Learners are thought to be active conceptualizers. They need to be actively engaged and to develop skills in analysis, synthesis and evaluation as part of their course requirements (Institute for Higher Education Policy, 2000). They can manipulate and organize resources while interacting in the inquiry tasks (Grabe, M. and Grabe, C., 2004). They can then synthesize, evaluate and reflect on how they develop skills, knowledge and values in their subject areas.
In contrast to conventional paper-based assessment, more interaction is likely to occur in online assessment. This is particularly true when online assessment is used as a formative evaluation tool, and it contributes to learning by providing feedback relating to performance. In general, it can be said that the contribution to learning provided by assessment will be enhanced by better learner engagement through improving the interactivity of the assessment.
Interaction comes in many different forms. Swan (2003) explains interaction as "the reciprocal events involving at least two actors and/or objects and at least two actions in which the actors, objects, and events mutually influence each other" (p.4). She sees e-learning as being able to facilitate at least three main kinds of learning-enhancing interaction: interaction with content, with instructors and with peers.
We employ Swan's model (drawn from Moore (1989)) to investigate the interactivity in online assessments. Figure 1 illustrates how, under the model, a student can act on and obtain responses in all three areas: content, peers and instructors.
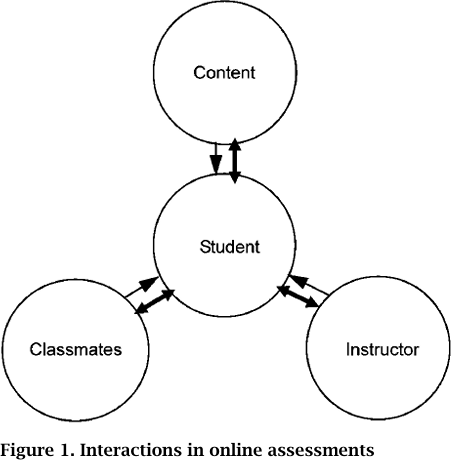
Online assessments, for the purpose of this study, may employ either a formative or summative function. Here are some examples of online assessment:
1. Content: online quizzes and exercises can be used for students to assess their understanding of content materials. Students may be allowed multiple attempts to interact with quizzes in a question bank or clarify misunderstandings though feedback on incorrect answers.
2. Peers: forums can be provided for students to take part in discussions on assigned topics. Individual or group contributions to the forum can be assessed quantitatively and/or qualitatively.
3. Instructors: the online submission of assignments can allow both learners and instructors to discuss areas for improvement before the final submission and grading.a
 الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















