

Grammar


Tenses


Present

Present Simple

Present Continuous

Present Perfect

Present Perfect Continuous


Past

Past Simple

Past Continuous

Past Perfect

Past Perfect Continuous


Future

Future Simple

Future Continuous

Future Perfect

Future Perfect Continuous


Parts Of Speech


Nouns

Countable and uncountable nouns

Verbal nouns

Singular and Plural nouns

Proper nouns

Nouns gender

Nouns definition

Concrete nouns

Abstract nouns

Common nouns

Collective nouns

Definition Of Nouns

Animate and Inanimate nouns

Nouns


Verbs

Stative and dynamic verbs

Finite and nonfinite verbs

To be verbs

Transitive and intransitive verbs

Auxiliary verbs

Modal verbs

Regular and irregular verbs

Action verbs

Verbs


Adverbs

Relative adverbs

Interrogative adverbs

Adverbs of time

Adverbs of place

Adverbs of reason

Adverbs of quantity

Adverbs of manner

Adverbs of frequency

Adverbs of affirmation

Adverbs


Adjectives

Quantitative adjective

Proper adjective

Possessive adjective

Numeral adjective

Interrogative adjective

Distributive adjective

Descriptive adjective

Demonstrative adjective


Pronouns

Subject pronoun

Relative pronoun

Reflexive pronoun

Reciprocal pronoun

Possessive pronoun

Personal pronoun

Interrogative pronoun

Indefinite pronoun

Emphatic pronoun

Distributive pronoun

Demonstrative pronoun

Pronouns


Pre Position


Preposition by function

Time preposition

Reason preposition

Possession preposition

Place preposition

Phrases preposition

Origin preposition

Measure preposition

Direction preposition

Contrast preposition

Agent preposition


Preposition by construction

Simple preposition

Phrase preposition

Double preposition

Compound preposition

prepositions


Conjunctions

Subordinating conjunction

Correlative conjunction

Coordinating conjunction

Conjunctive adverbs

conjunctions


Interjections

Express calling interjection

Phrases

Sentences


Grammar Rules

Passive and Active

Preference

Requests and offers

wishes

Be used to

Some and any

Could have done

Describing people

Giving advices

Possession

Comparative and superlative

Giving Reason

Making Suggestions

Apologizing

Forming questions

Since and for

Directions

Obligation

Adverbials

invitation

Articles

Imaginary condition

Zero conditional

First conditional

Second conditional

Third conditional

Reported speech

Demonstratives

Determiners


Linguistics

Phonetics

Phonology

Linguistics fields

Syntax

Morphology

Semantics

pragmatics

History

Writing

Grammar

Phonetics and Phonology

Semiotics


Reading Comprehension

Elementary

Intermediate

Advanced


Teaching Methods

Teaching Strategies

Assessment
On graduate qualities and course objectives
المؤلف:
Sue Gelade & Frank Fursenko
المصدر:
Enhancing Teaching and Learning through Assessment
الجزء والصفحة:
P482-C40
2025-08-29
339
On graduate qualities and course objectives
We would argue that in an appropriately designed course graduate qualities should shape course objectives, which in turn should shape assessment tasks and, assessment tasks should develop graduate qualities - as shown in Figure 1.
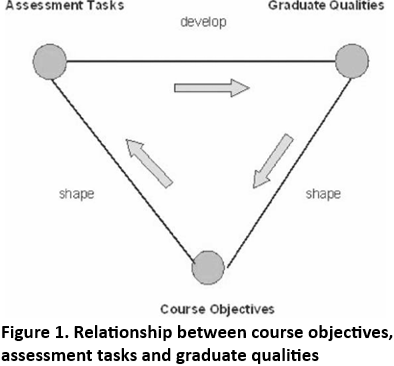
However, the mapping exercise revealed that in some courses there is little or no correlation between the three categories (assessment tasks, course objectives and graduate qualities) under consideration. It would appear that the majority of assessment tasks we mapped require students to understand and apply the content taught. If we use Bloom's cognitive domain as a guide, these assessment tasks assume that students have been guided or have learned to take their first level knowledge acquisition through the comprehension level to the application level. It is important to note here that this third level assumes that students have developed sound problem solving skills - one of the intrinsic graduate qualities. The mapping exercise indicated though, that students' previous assessments did not appear to offer them incremental development throughout their courses and did not tackle the various cognitive skills in an apparently linear formation.
A further analysis of graduate qualities in relation to the cognitive domain of Bloom's Taxonomy reveals that graduate qualities explicitly assume the first four levels of Bloom's Taxonomy (knowledge, comprehension, application and analysis) but not the top two levels. Depending on one's interpretation, the top two levels (synthesis and evaluation) are implicitly assumed in the graduate qualities. This finding was surprising given that the top two levels of Bloom's Taxonomy distinguish a traditional university education based competence from tertiary college training that emphasizes the acquisition of a skill set of competencies.
If assessment tasks determine the development of students for the real world which they enter on graduation, then graduate qualities should reflect the modern economy.
As part of the analysis of data obtained from our research, we needed to determine whether the graduate qualities provide an effective framework for the development of students in a modern, global knowledge economy. A knowledge economy is defined by the following characteristics:
1. Knowledge is the key factor in production.
2. Improving human capital is critical for GDP growth.
3. "know-why" and "know-how" is more important than know why.
4. Knowledge gained by experience is as important as formal education and training.
5. Life long learning is vital for organizations and individuals.
6.ICT releases people's creative potential and knowledge.
7. Globalization (Ministry NZ, 2005).
An analysis of the university's graduate qualities shows them as consistent with the demands of a knowledge economy and therefore they provide a suitable framework for shaping course objectives, which in turn should shape assessment tasks. Our findings provide some support to our conclusions that graduate qualities are a very useful framework for preparing students for a modern global knowledge economy.
Crucially, our work has shown (see Our findings Figure 3) that Graduate Qualities 4 'Ethical Action and Social Considerations' and 7 'International Perspectives' are those least likely to be built into course objectives or assessment tasks. Yet these closely related qualities indicate the extent to which graduates are prepared for addressing all stakeholder needs in a modern, global knowledge economy.
 الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
الاكثر قراءة في Teaching Strategies
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















