

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Water
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
الجزء والصفحة:
406
2025-09-10
102
Water
Key point: Hydrogen bonding in water results in a high boiling liquid and a highly structured arrangement in the solid, ice. At least nine distinct forms of ice have been identified. At 0C and atmospheric pressure, hexagonal ice Ih forms (Fig. 10.7) but between 120 and 140C the cubic form, Ic , is produced. At very high pressures several higher density polymorphs are formed,
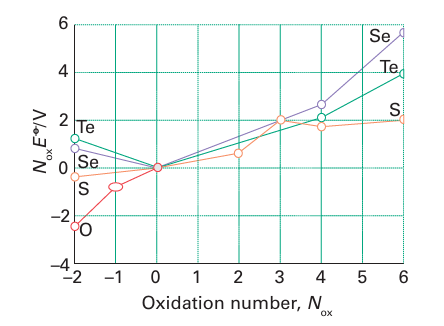
Figure. 16.2 Frost diagram for the elements of Group 16 in acidic solution. The species with oxidation number -2 are H2 E. For oxidation number -1 the compound is H2O2. The positive oxidation numbers refer to the oxo acids or oxoanions. some of which are based on silica-like structures (Section 14.10). Water is formed by the direct interaction of the elements: 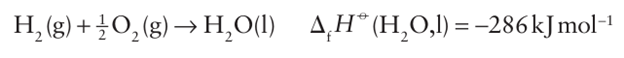
This reaction is very exothermic and provides the basis for the development of the hydrogen economy and hydrogen fuel cells (Fig. 5.1, Box 10.2, and Section 24.1). Water is the most widely used solvent not only because it is so widely available but also because of its high relative permittivity (dielectric constant), wide liquid range, and—through a combination of its polar character and ability to form hydrogen bonds—solvating ability. Many anhydrous and hydrated com pounds dissolve in water to give hydrated cations and anions. Some predominantly covalent compounds, such as ethanol and ethanoic (acetic) acid, are soluble in water or miscible with it because of hydrogen-bonded interactions with the solvent. Many other covalent compounds react with water in hydrolysis reactions; examples are discussed in the appropriate chapters. In addition to simple dissolution and hydrolysis reactions, the importance of aqueous solution chemistry can be seen in redox reactions and acid base reactions. Water also acts as a Lewis base ligand in metal complexes (Section 7.1). The deprotonated forms, OH- and particularly the oxide ion O2- are important ligands for stabilizing higher oxidation states, examples of which are found in the simple oxo-cations of early d-block elements, such as the vanadyl ion, VO+2.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















