

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Energetics
المؤلف:
Peter Atkins, Tina Overton, Jonathan Rourke, Mark Weller, and Fraser Armstrong
المصدر:
Shriver and Atkins Inorganic Chemistry ,5th E
الجزء والصفحة:
691
2025-10-16
58
Energetics
Key point: A catalyst increases the rates of processes by introducing new pathways with lower Gibbs energies of activation; the reaction profile contains no high peaks and no deep troughs. A catalyst increases the rates of processes by introducing new pathways with lower Gibbs energies of activation, ∆‡G. We need to focus on the Gibbs energy profile of a catalytic reaction, not just the enthalpy or energy profile, because the new elementary steps that occur in the catalysed process are likely to have quite different entropies of activation. A catalyst does not affect the Gibbs energy of the overall reaction, ∆rGO, because G is a state function.1 The difference is illustrated in Fig. 26.1, where the overall reaction Gibbs energy is the same in both energy profiles. Reactions that are thermodynamically unfavourable cannot be made favourable by a catalyst. Figure 26.1 also shows that the Gibbs energy profile of a catalysed reaction contains no high peaks and no deep troughs. The new pathway introduced by the catalyst changes the mechanism of the reaction to one with a very different shape and with lower maxima. However, an equally important point is that stable or nonlabile catalytic intermediates do not occur in the cycle. Similarly, the product must be released in a thermodynamically favourable step. If, as shown by the blue line in Fig. 26.1, a stable complex were formed with the catalyst, it would turn out to be the product of the reaction and the cycle would terminate. Similarly, impurities may suppress catalysis by coordinating strongly to catalytically active sites and act as catalyst poisons.
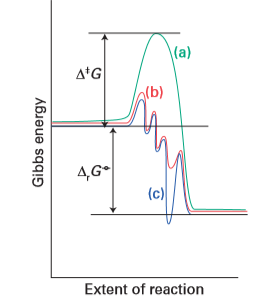
Figure 26.1 Schematic representation of the energetics of a catalytic cycle. The uncatalysed reaction (a) has a higher ∆‡G than a step in the catalysed reaction (b). The Gibbs energy of the overall reaction, ∆rGO, is the same for routes (a) and (b). The curve (c) shows the profile for a reaction mechanism with an intermediate that is more stable than the product.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















