
Pure Substances and Mixtures
 المؤلف:
John T. Moore, EdD
المؤلف:
John T. Moore, EdD
 المصدر:
Chemistry Essentials For Dummies
المصدر:
Chemistry Essentials For Dummies
 الجزء والصفحة:
p10
الجزء والصفحة:
p10
 17-2-2016
17-2-2016
 4156
4156
Pure Substances and Mixtures
One of the basic processes in science is classification. In this section, we explain how all matter can be classified as either a pure substance or a mixture (see Figure 1).
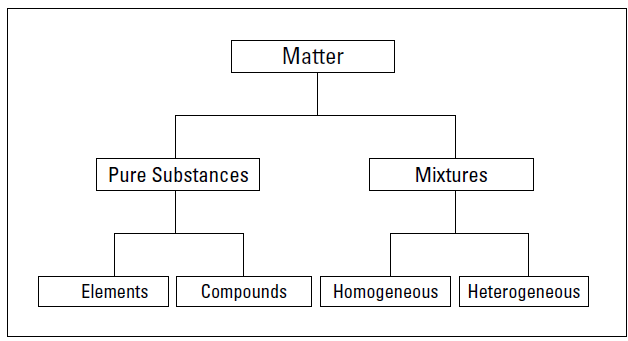
Figure 1: Classifying of matter.
Pure substances
A pure substance, like salt or sugar, has a definite and constant composition or makeup. A pure substance can be either an element or a compound, but the composition of a pure substance doesn’t vary.
Elements
An element is composed of a single kind of atom. An atom is the smallest particle of an element that still has all the properties of the element. For instance, if you slice and slice a chunk of the element gold until only one tiny particle is left that can’t be chopped anymore without losing the properties that make gold gold, then you have an atom. (I discuss properties later in the section “Nice Properties You’ve Got There.”)
The atoms in an element all have the same number of protons. Protons are subatomic particles — particles of an atom.
The important thing to remember right now is that elements are the building blocks of matter.
Compounds
A compound is composed of two or more elements in a specific ratio. For example, water (H2O) is a compound made up of two elements, hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O). These elements are combined in a very specific way — in a ratio of two hydrogen atoms to one oxygen atom (hence, H2O). A lot of compounds contain hydrogen and oxygen, but only one has that special 2-to-1 ratio called water.
A compound has physical and chemical properties different from the elements that make it up. For instance, even though water is made up of hydrogen and oxygen, water’s properties are a unique combination of the two elements. Chemists can’t easily separate the components of a compound: They have to resort to some type of chemical reaction.
 الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


