

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Lewis structures
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p26
18-2-2016
3294
Lewis structures
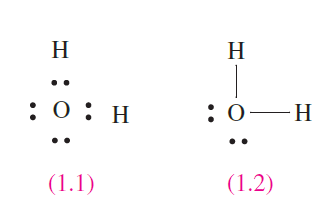
Lewis presented a simple, but useful, method of describing the arrangement of valence electrons in molecules. The approach uses dots (or dots and crosses) to represent the number of valence electrons, and the nuclei are indicated by appropriate elemental symbols. A basic premise of the theory is that electrons in a molecule should be paired; the presence of a single (odd) electron indicates that the species is a radical. Diagram 1.1 shows the Lewis structure for H2O with the O-H bonds designated by pairs of dots (electrons); an alternative representation is given in structure 1.2 where each line stands for one pair of electrons, i.e. a single covalent bond. Pairs of valence electrons which are not involved in bonding are lone pairs.

The Lewis structure for N2 shows that the N-N bond is composed of three pairs of electrons and is a triple bond (structures 1.3 and 1.4). Each N atom has one lone pair of electrons. The Lewis structures 1.5 and 1.6 for O2 indicate the presence of a double bond, with each O atom bearing two lone pairs of electrons.


Lewis structures give the connectivity of an atom in a molecule, the bond order and the number of lone pairs and these may be used to derive structures using the valenceshell electron-pair repulsion model .
 الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
الاكثر قراءة في الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















