

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Poliomyelitis
المؤلف:
اعداد المرجع الالكتروني للمعلوماتية
المصدر:
almerja.com
الجزء والصفحة:
29-2-2016
2942
Poliomyelitis
Causative agent poliovirus is the member of the family picornaviridae which is one of the largest and most important families of human pathogens .these are smallest RNA viruses .Despite a member of enterovirus poliovirus as well as other enterovirus don’t produce enteric disease they are named because the alimentary canal is their predominant site of replication
Vaccine against poliomyelitis
There are two kinds of vaccines for immunization against virus
- a vaccine mad of noninfectious virus particles ( killed or inactivated virus vaccine administered by injection referred to as killed poliovaccine KPV or inactivated poliovaccine IPV )
- made of infectious virus particles attenuated in neurovirulence (live attenuated virus vaccine LPV administered orally referred to as live poliovaccine or oral poliovaccine OPV )
Oral polio virus vaccine
the trivalent oral poliovirus vaccine TOPV is mixture of three types (monovalent ) of attenuated polioviruses which are propagated separately in appropriate cell cultures and then mixed .A stabilizer magnesium chloride is added to this blended mixture .Each dose contains less than 25μg of each of the antibiotics ,streptomycin and neomycin .phenol added as indicator of the PH, before being released by the manufacturer the vaccine in final containers is kept continuously in the frozen temperature below -20 C .under this condition of storage ,the expiry date of vaccine is fixed which is not more than two years. after thawing OPV may be refrigerated at temperature of 2-8 C for a period not exceeding 30 days .
inactivated poliovirus vaccine
this vaccine contains 40,8 and 32 D unit respectively of type 1,2 and 3 in each dose of the vaccine which gives adequate immunity after two doses given parenterally
Advantages with IPV
- confers humoral immunity in a satisfactory proportion of vaccines if a sufficient number of doses are given .
- incorporated into regular pediatric immunization with other DPT
- Absence of living virus precludes potential mutation and reversion to virulence
- Absence of living virus permits it is use in immunodeficient or immunosuppressed individuals and their households .
- Reduced the spread of polioviruses in small countries where it has been properly used
Disadvantage of IPV
- repeated boosters required to maintain detectable ab level
- doesn’t induce local (intestinal ) immunity in the vaccine
- more costly than OPV
Advantage with OPV
- confers humoral both systemic and intestinal immunity like natural infection
- immunity that induced may be life long
- oral administered is more acceptable to vaccine than injection and easier to accomplish
Disadvantage with OPV
- being live viruses the vaccine viruses do mutate and in rare instance have reverted towards neurovirulence significantly to cause paralytic inreciepients or their contacts
- vaccine progeny virus spread to household contact
- contraindication in those with immunedeficiency disorder and their household contact as well as individuals under going immunossupression therapy
Differences between OPV and IPV
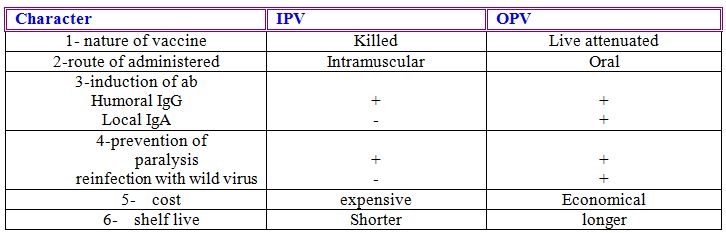
Efficacy of poliovirus vaccine
The presence of humoral antibodies has been seen after 7-15 years of immunization with IPV
IPV has also been shown to induce good protection in persons in tropical countries where OPV may fail to uniformly immunize because of the presence of the inhibitors of the vaccine virus in the gastrointestinal tract especially in developing tropical countries .
OPV : the persistence of humoral ab after vaccinating with OPV has been reported up to 15 years or even more . Seroconversion in virtually 100% recipients .There are several problems with OPV such as occurrence of vaccine associated paralytic poliomyelitis cases in developed countries and failure of OPV to cause seroconversion .
OPV is unstable unless kept at very low temperature .Current recommendations indicate that after thawing ,OPV be held at no more than 10 C for less than 30 days .At 0-8 C the virus can be stored for 6-12 months without a loss in titre.
Immunization schedules
OPV : the centres for disease control (CDC) recommends that primary immunization with OPV should commence at the age of two months ,the second and third doses should be given at 2 months interval there after ,and fourth dose should be given at 18 months of age .
If the child vomits within one hour of receiving the oral poliovaccine a further dose may be given the next day .
Contraindication to OPV
1-Acute febrile illness b- sever diarrhea and vomiting c- Sensitivity to antimicrobial agents in vaccine preparation
d- Immunodeficiency and malignancy e- pregnancy f- If there has been a serious reaction t o a previous vaccination with OPV eg .anaphylactic reaction
Adverse reactions
Vaccine associated paralysis in recipients is very rare about one in 2 million doses administration
IPV : The CDC recommends first dose of IPV at 6-12 weeks of age followed by two doses after intervals of 4-8 weeks .The fourth dose is recommended after 6-12 months of the third dose and supplementary booster at the age of 4-6 years ,Subsequent boosters may be administered every five years till the age of 18 years .
 الاكثر قراءة في اللقاحات
الاكثر قراءة في اللقاحات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















