

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The valence bond (VB) model applied to F2, O2 and N2
المؤلف:
CATHERINE E. HOUSECROFT AND ALAN G. SHARPE
المصدر:
Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
p28
8-3-2016
2043
The valence bond (VB) model applied to F2, O2 and N2
Consider the formation of F2. The ground state electronic configuration of F is [He]2s2 2p5, and the presence of the single unpaired electron indicates the formation of an F_ F single bond. We can write down resonance structures 1.12 to describe the bonding in F2, with the expectation that the covalent contribution will predominate.

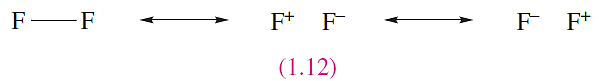
The formation of O2 involves the combination of two O atoms with ground state electronic configurations of 1s2 2s2 2p4. Each O atom has two unpaired electrons and so VB theory predicts the formation of an O=O double bond.
Since VB theory works on the premise that electrons are paired wherever possible, the model predicts that O2 is diamagnetic. One of the notable failures of VB theory is its inability to predict the observed paramagnetism of O2. As we shall see, molecular orbital theory is fully consistent with O2 being a diradical. When two N atoms ([He]2s2 2p3) combine to give N2, an N≡N triple bond results. Of the possible resonance structures, the predominant form is covalent and this gives a satisfactory picture of the bonding in N2. In a diamagnetic species, all electrons are spin-paired; a diamagnetic substance is repelled by a magnetic field. A paramagnetic species contains one or more unpaired electrons; a paramagnetic substance is attracted by a magnetic field.
 الاكثر قراءة في نظريات التآصر الكيميائي
الاكثر قراءة في نظريات التآصر الكيميائي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















