

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Quinolones
المؤلف:
اعداد المرجع الالكتروني للمعلوماتية
المصدر:
almerja.com
الجزء والصفحة:
24-3-2016
6917
Quinolones
The classification of the quinolones into "generations" on the basis of microbiological activity is controversial, but is useful for practicing clinicians.
According to this classification, nalidixic acid is o first-generation quinolone. Because of its reliable activity against most Enterobactericeae, it became o popular choice for the treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infections. Nalidixic acid is also used to treat shigellosis in children. lt requires dosing four times a day and is available only as an oral agent and does not achieve significant tissue levels. it hos no activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, anaerobes, chlamydia, mycoplasmas or Gram-positive bacteria.
The second-generation quinolones expanded the bacterial coverage to include Pseudomonas aeruginosa and staphylococci. These quinolones have modest-to-poor activity against streptococci (notably Streptococcus pneumoniae and enterococci) and anaerobes. They exhibit high intracellular penetration, allowing for therapy against intracellular organisms like chlamydia, mycoplasmas and legionellae.
A significant problem has been the emergence of resistance during therapy for infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus viridans. The second-generation quinolones can be divided into two subgroups. One group contains ciprofloxacin and ofloxacin, which are available in both oral and parenteral formulation. and can be used to treat minor and severe infections such as urinary tract infections. severe enteric infections caused by salmonellae or Shigella, gonorrhoeae and typhoid fever. The other group contains agents available only as oral formulations (e.g. enoxacin, lomefloxacin, norfloxacin), which are used primarily for urinary tract infections. ln general, these agents should be reserved for treatment of significant infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa or other Gram-negative bacteria which are resistant to conventional antibiotics.
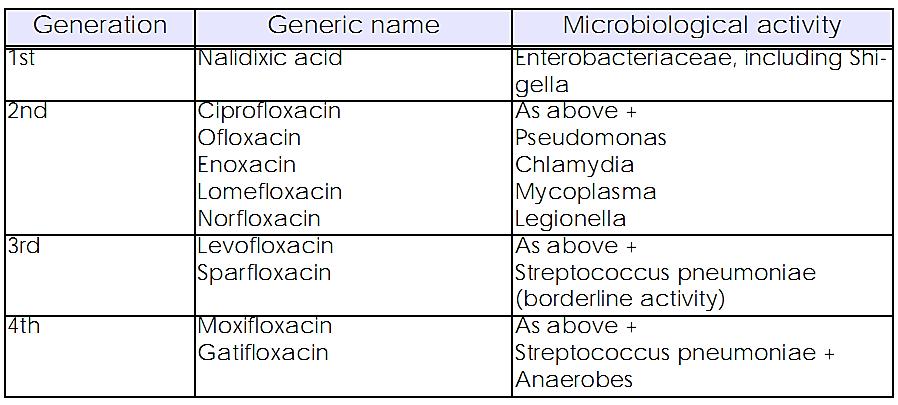
The third-generation quinolones have similar activity to the second-generation quinolones. plus increased activity against Streptococcus pneumoniae. However, they are less active than the second-generation quinolones against Gram-negative bacteria. Activity against anaerobes is modest-to-poor. Levofloxacin and sparfloxacin belong to this group of quinolones. These quinolones should ideally be reserved for use as alternatives to other agents for acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis and bacterial pneumonia in elderly patients.
Moxifloxacin and gatifloxacin can be considered fourth-generation quinolones owing to their activity against anaerobes, and significantly increased activity against Streptococcus pneumoniae. Hence, these might be considered for the treatment of intraabdominal infections (of intestinal or pelvic origin) in addition to respiratory tract infections (as for the third generation quinolones).
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















