

تاريخ الرياضيات

الاعداد و نظريتها

تاريخ التحليل

تار يخ الجبر

الهندسة و التبلوجي


الرياضيات في الحضارات المختلفة

العربية

اليونانية

البابلية

الصينية

المايا

المصرية

الهندية


الرياضيات المتقطعة

المنطق

اسس الرياضيات

فلسفة الرياضيات

مواضيع عامة في المنطق


الجبر

الجبر الخطي

الجبر المجرد

الجبر البولياني

مواضيع عامة في الجبر

الضبابية

نظرية المجموعات

نظرية الزمر

نظرية الحلقات والحقول

نظرية الاعداد

نظرية الفئات

حساب المتجهات

المتتاليات-المتسلسلات

المصفوفات و نظريتها

المثلثات


الهندسة

الهندسة المستوية

الهندسة غير المستوية

مواضيع عامة في الهندسة

التفاضل و التكامل


المعادلات التفاضلية و التكاملية

معادلات تفاضلية

معادلات تكاملية

مواضيع عامة في المعادلات


التحليل

التحليل العددي

التحليل العقدي

التحليل الدالي

مواضيع عامة في التحليل

التحليل الحقيقي

التبلوجيا

نظرية الالعاب

الاحتمالات و الاحصاء

نظرية التحكم

بحوث العمليات

نظرية الكم

الشفرات

الرياضيات التطبيقية

نظريات ومبرهنات


علماء الرياضيات

500AD

500-1499

1000to1499

1500to1599

1600to1649

1650to1699

1700to1749

1750to1779

1780to1799

1800to1819

1820to1829

1830to1839

1840to1849

1850to1859

1860to1864

1865to1869

1870to1874

1875to1879

1880to1884

1885to1889

1890to1894

1895to1899

1900to1904

1905to1909

1910to1914

1915to1919

1920to1924

1925to1929

1930to1939

1940to the present

علماء الرياضيات

الرياضيات في العلوم الاخرى

بحوث و اطاريح جامعية

هل تعلم

طرائق التدريس

الرياضيات العامة

نظرية البيان
INTRODUCTION-A GEOMETRIC SOLUTION.
المؤلف:
Lawrence C. Evans
المصدر:
An Introduction to Mathematical Optimal Control Theory
الجزء والصفحة:
10-12
3-10-2016
1123
To illustrate how actually to solve a control problem, in this last section we introduce some ad hoc calculus and geometry methods for the rocket car problem, Example 5 in(EXAMPLES).
First of all, let us guess that to find an optimal solution we will need only to consider the cases a = 1 or a = −1. In other words, we will focus our attention only upon those controls for which at each moment of time either the left or the right rocket engine is fired at full power.
CASE 1: Suppose first that α ≡ 1 for some time interval, during which

And so

Let t0 belong to the time interval where α ≡ 1 and integrate from t0 to t:

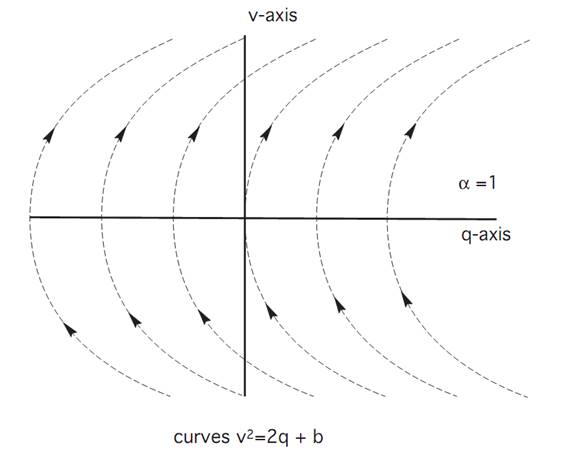
In other words, so long as the control is set for α ≡ 1, the trajectory stays on the curve v2 = 2q + b for some constant b.
CASE 2: Suppose now α ≡ −1 on some time interval. Then as above

And hence

Let t1 belong to an interval where α ≡ −1 and integrate:

Consequently, as long as the control is set for α ≡ −1, the trajectory stays on the curve v2 = −2q + c for some constant c.

GEOMETRIC INTERPRETATION. Formula (1.1) says if α ≡ 1, then (q(t), v(t)) lies on a parabola of the form
v2= 2q + b.
Similarly, (1.2) says if α ≡ −1, then (q(t), v(t)) lies on a parabola
v2= −2q + c.
Now we can design an optimal control α∗(.), which causes the trajectory to jump between the families of right– and left–pointing parabolas, as drawn. Say we start at the black dot, and wish to steer to the origin. This we accomplish by first setting the control to the value α = −1, causing us to move down along the second family of parabolas. We then switch to the control α = 1, and thereupon move to a parabola from the first family, along which we move up and to the left, ending up at the origin. See the picture.
References
[B-CD] M. Bardi and I. Capuzzo-Dolcetta, Optimal Control and Viscosity Solutions of Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman Equations, Birkhauser, 1997.
[B-J] N. Barron and R. Jensen, The Pontryagin maximum principle from dynamic programming and viscosity solutions to first-order partial differential equations, Transactions AMS 298 (1986), 635–641.
[C1] F. Clarke, Optimization and Nonsmooth Analysis, Wiley-Interscience, 1983.
[C2] F. Clarke, Methods of Dynamic and Nonsmooth Optimization, CBMS-NSF Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics, SIAM, 1989.
[Cr] B. D. Craven, Control and Optimization, Chapman & Hall, 1995.
[E] L. C. Evans, An Introduction to Stochastic Differential Equations, lecture notes avail-able at http://math.berkeley.edu/˜ evans/SDE.course.pdf.
[F-R] W. Fleming and R. Rishel, Deterministic and Stochastic Optimal Control, Springer, 1975.
[F-S] W. Fleming and M. Soner, Controlled Markov Processes and Viscosity Solutions, Springer, 1993.
[H] L. Hocking, Optimal Control: An Introduction to the Theory with Applications, OxfordUniversity Press, 1991.
[I] R. Isaacs, Differential Games: A mathematical theory with applications to warfare and pursuit, control and optimization, Wiley, 1965 (reprinted by Dover in 1999).
[K] G. Knowles, An Introduction to Applied Optimal Control, Academic Press, 1981.
[Kr] N. V. Krylov, Controlled Diffusion Processes, Springer, 1980.
[L-M] E. B. Lee and L. Markus, Foundations of Optimal Control Theory, Wiley, 1967.
[L] J. Lewin, Differential Games: Theory and methods for solving game problems with singular surfaces, Springer, 1994.
[M-S] J. Macki and A. Strauss, Introduction to Optimal Control Theory, Springer, 1982.
[O] B. K. Oksendal, Stochastic Differential Equations: An Introduction with Applications, 4th ed., Springer, 1995.
[O-W] G. Oster and E. O. Wilson, Caste and Ecology in Social Insects, Princeton UniversityPress.
[P-B-G-M] L. S. Pontryagin, V. G. Boltyanski, R. S. Gamkrelidze and E. F. Mishchenko, The Mathematical Theory of Optimal Processes, Interscience, 1962.
[T] William J. Terrell, Some fundamental control theory I: Controllability, observability, and duality, American Math Monthly 106 (1999), 705–719.
 الاكثر قراءة في نظرية التحكم
الاكثر قراءة في نظرية التحكم
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















