
Crystals
 المؤلف:
Jerome L. Rosenberg and Lawrence M. Epstein
المؤلف:
Jerome L. Rosenberg and Lawrence M. Epstein
 المصدر:
College Chemistry
المصدر:
College Chemistry
 الجزء والصفحة:
p 75
الجزء والصفحة:
p 75
 9-7-2017
9-7-2017
 1846
1846
Crystals
A piece of the crystal structure of NaCl, called the unit cell, is shown in Figure 1.1. The Cl- ions are represented by shaded spheres, the Na+ ions by smaller white spheres. The unit cell is the smallest unit of the crystal which can be replicated to form the entire crystal. Thus if we duplicate the unit cell and superimpose the left-hand face of the duplicate on the right-hand face of the original, we have two unit cells of the crystal. If we do the same thing top to bottom, front to back, and continue many, many times, we will have the NaCl lattice.
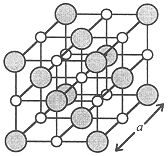
Figure 1.1. The Unit Cell of the Sodium Chloride Lattice
Notice that each Na+ ion is surrounded by six Cl- ions and each Cl- ion is surrounded by six Na+ ions. We say that the coordination number of Na+ or Cl- is 6, i.e., there are six nearest neighbor Cl- or Na+ ions around each Na+ or Cl- ion. There are 14 Cl- ions, 8 at the corners and 6 centered on the faces; but only 13 Na+ ions, 12 on the edges and 1 in the center of the unit cell. Ions on faces, edges, or corners are shared with the next cell. Ions on the corners are shared among 8 unit cells so that only 1/8 of each corner ion belongs to this unit cell. Similarly, ions centered on faces are shared by 2 cells so that 1/2 of each face ion belongs to this cell. Ions on edges are shared by 4 unit cells so that 1/4 of each edge ion belongs the this cell. An ion in the center belongs to this cell only. Revising the count, we have
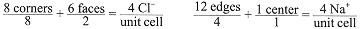
or four NaCl units per unit cell.
If we know the structure of a unit cell, we can use the molar mass and density to compute the dimensions of the unit cell. For example, NaCl (58.44 g/mol) has density 2.165 g/cm3. The molar volume is:

The volume of 4 NaCl units is the volume of one unit cell,
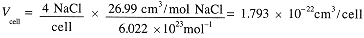
Taking the cube root, we have the unit cell dimension, a = 5.639 × 10-8 cm or 563.9 pm. The closest Na+-Cldistance then is 281.9 pm. This distance can be regarded as the sum of the ionic radii of Na+ and Cl-. Using similar results from many other ionic crystals, the radii of many ions have been determined. A few of these are given in Table 1.1.
Table 1.1. Some Ionic Radii in pm

 الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
الاكثر قراءة في مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


