

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Preparation and Reactions : Three-Membered Rings
المؤلف:
William Reusch
المصدر:
Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry
الجزء والصفحة:
............
29-7-2018
2632
Preparation and Reactions
Three-Membered Rings
Oxiranes (epoxides) are the most commonly encountered three-membered heterocycles. Epoxides are easily prepared by reaction of alkenes with peracids, usually with good stereospecificity. Because of the high angle strain of the three-membered ring, epoxides are more reactive that unstrained ethers. Addition reactions proceeding by electrophilic or nucleophilic opening of the ring constitute the most general reaction class. Example 1 in the following diagram shows one such transformation, which is interesting due to subsequent conversion of the addition intermediate into the corresponding thiirane. The initial ring opening is stereoelectronically directed in a trans-diaxial fashion, the intermediate relaxing to the diequatorial conformer before cyclizing to a 1,3-oxathiolane intermediate.
Other examples show similar addition reactions to thiiranes and aziridines. The acid-catalyzed additions in examples 2 and 3, illustrate the influence of substituents on the regioselectivity of addition. Example 2 reflects the SN2 character of nucleophile (chloride anion) attack on the protonated aziridine (the less substituted carbon is the site of addition). The phenyl substituent in example 3 serves to stabilize the developing carbocation to such a degree that SN1 selectivity is realized. The reduction of thiiranes to alkenes by reaction with phosphite esters (example 6) is highly stereospecific, and is believed to take place by an initial bonding of phosphorous to sulfur.
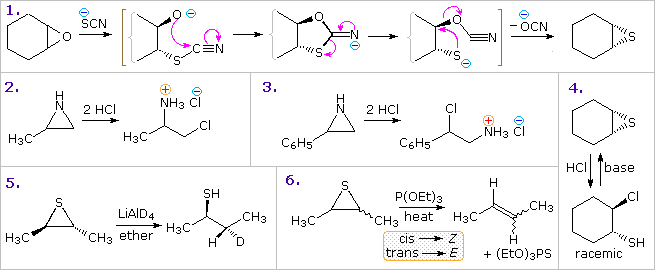
anoic acid (example 9) accounts both for the 1st-order kinetics of this reaction and the retention of configuration in the product. Note that two inversions of configuration at C-2 result in overall retention. Many examples of intramolecular interactions, such as example 10, have been documented.
An interesting regioselectivity in the intramolecular ring-opening reactions of disubstituted epoxides having a pendant γ-hydroxy substituent has been noted. As illustrated below, acid and base-catalyzed reactions normally proceed by 5-exo-substitution (reaction 1), yielding a tetrahydrofuran product. However, if the oxirane has an unsaturated substituent (vinyl or phenyl), the acid-catalyzed opening occurs at the allylic (or benzylic) carbon (reaction 2) in a 6-endo fashion. The π-electron system of the substituent assists development of positive charge at the adjacent oxirane carbon, directing nucleophilic attack to that site.
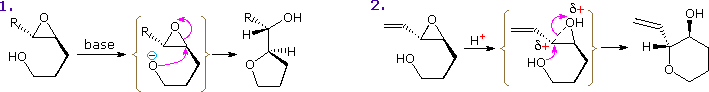
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















