


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 6-8-2019
Date: 19-8-2019
Date: 12-1-2022
|
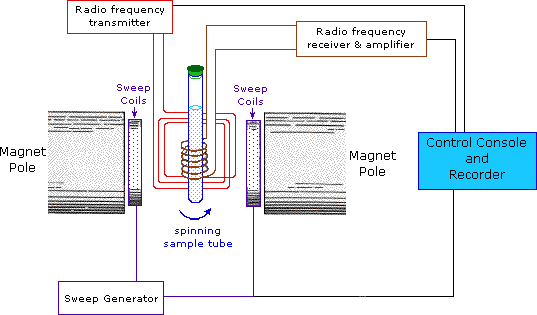
Proton NMR Spectroscopy
This important and well-established application of nuclear magnetic resonance will serve to illustrate some of the novel aspects of this method. To begin with, the nmr spectrometer must be tuned to a specific nucleus, in this case the proton. The actual procedure for obtaining the spectrum varies, but the simplest is referred to as the continuous wave (CW) method. A typical CW-spectrometer is shown in the following diagram. A solution of the sample in a uniform 5 mm glass tube is oriented between the poles of a powerful magnet, and is spun to average any magnetic field variations, as well as tube imperfections. Radio frequency radiation of appropriate energy is broadcast into the sample from an antenna coil (colored red). A receiver coil surrounds the sample tube, and emission of absorbed rf energy is monitored by dedicated electronic devices and a computer. An nmr spectrum is acquired by varying or sweeping the magnetic field over a small range while observing the rf signal from the sample. An equally effective technique is to vary the frequency of the rf radiation while holding the external field constant.
As an example, consider a sample of water in a 2.3487 T external magnetic field, irradiated by 100 MHz radiation. If the magnetic field is smoothly increased to 2.3488 T, the hydrogen nuclei of the water molecules will at some point absorb rf energy and a resonance signal will appear. An animation showing this may be activated by clicking the Show Field Sweep button. The field sweep will be repeated three times, and the resulting resonance trace is colored red. For visibility, the water proton signal displayed in the animation is much broader than it would be in an actual experiment.
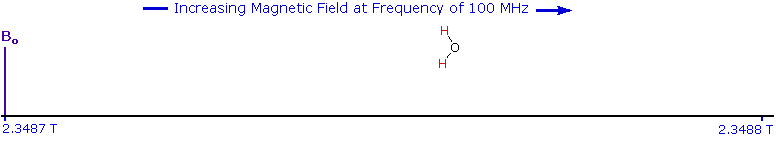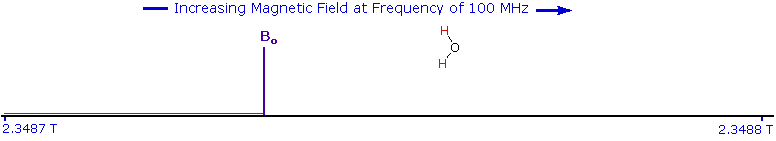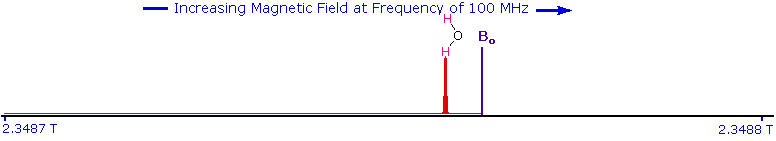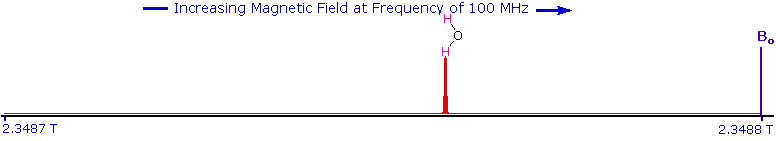
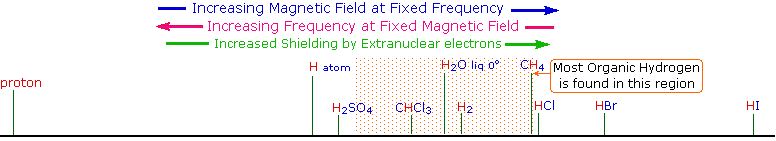
Since protons all have the same magnetic moment, we might expect all hydrogen atoms to give resonance signals at the same field / frequency values. Fortunately for chemistry applications, this is not true. By clicking the Show Different Protons button under the diagram, a number of representative proton signals will be displayed over the same magnetic field range. It is not possible, of course, to examine isolated protons in the spectrometer described above; but from independent measurement and calculation it has been determined that a naked proton would resonate at a lower field strength than the nuclei of covalently bonded hydrogens. With the exception of water, chloroform and sulfuric acid, which are examined as liquids, all the other compounds are measured as gases.
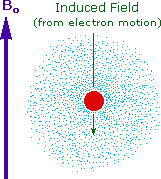



|
|
|
|
لصحة القلب والأمعاء.. 8 أطعمة لا غنى عنها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
حل سحري لخلايا البيروفسكايت الشمسية.. يرفع كفاءتها إلى 26%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
بالصور: بمناسبة تجديد الثقة له أمين عام للعتبة الحسينية…الاستاذ حسن رشيد العبايجي يستقبل الامين العام للعتبة العلوية والوفد المرافق له في الصحن الحسيني
|
|
|