

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Resonance Contributors for the Carboxylate Group
المؤلف:
........
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
الجزء والصفحة:
............
10-5-2019
2154
Resonance Contributors for the Carboxylate Group
The convention of drawing two or more resonance contributors to approximate a single structure may seem a bit clumsy to you at this point, but as you gain experience you will see that the practice is actually very useful when discussing the manner in which many functional groups react. Let’s next consider the carboxylate ion (the conjugate base of a carboxylic acid). As our example, we will use formate, the simplest possible carboxylate-containing molecule. The conjugate acid of formate is formic acid, which causes the painful sting you felt if you have ever been bitten by an ant.
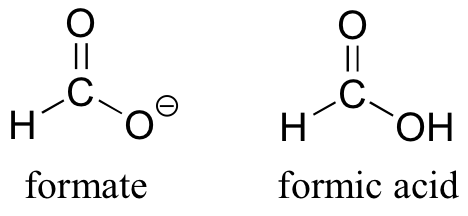
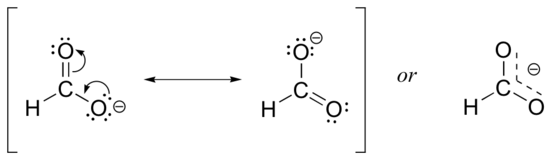
Usually, you will see carboxylate groups drawn with one carbon-oxygen double bond and one carbon-oxygen single bond, with a negative formal charge located on the single-bonded oxygen. In actuality, however, the two carbon-oxygen bonds are the same length, and although there is indeed an overall negative formal charge on the group, it is shared equally between the two oxygens. Therefore, the carboxylate can be more accurately depicted by a pair of resonance contributors. Alternatively, a single structure can be used, with a dashed line depicting the resonance-delocalized pi bond and the negative charge located in between the two oxygens.
Let’s see if we can correlate these drawing conventions to a valence bond theory picture of the bonding in a carboxylate group. We know that the carbon must be sp2-hybridized, (the bond angles are close to 120˚, and the molecule is planar), and we will treat both oxygens as being sp2-hybridized as well. Both carbon-oxygen sigma bonds, then, are formed from the overlap of carbon sp2 orbitals and oxygen sp2 orbitals.
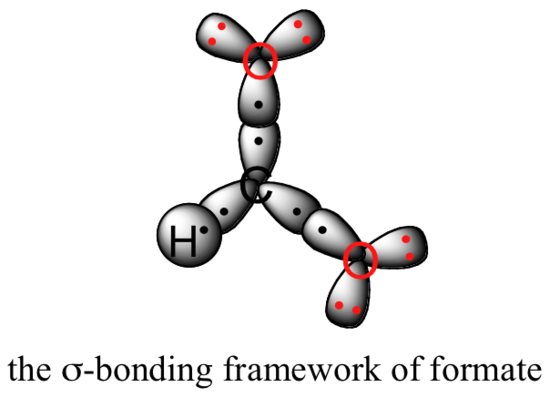
In addition, the carbon and both oxygens each have an unhybridized 2pz orbital situated perpendicular to the plane of the sigma bonds. These three 2pz orbitals are parallel to each other, and can overlap in a side-by-side fashion to form a delocalized pi bond.
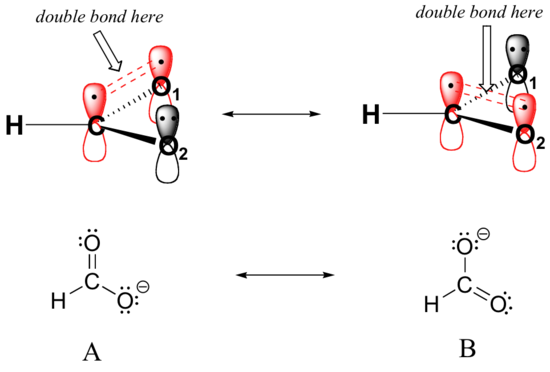
Resonance contributor A shows oxygen #1 sharing a pair of electrons with carbon in a pi bond, and oxygen #2 holding a lone pair of electrons in its 2pz orbital. Resonance contributor B, on the other hand, shows oxygen #2 participating in the pi bond with carbon, and oxygen #1 holding a lone pair in its 2pz orbital. Overall, the situation is one of three parallel, overlapping 2pz orbitals sharing four delocalized pi electrons. Because there is one more electron than there are 2pz orbitals, the system has an overall charge of –1. This is the kind of 3D picture that resonance contributors are used to approximate, and once you get some practice you should be able to quickly visualize overlapping 2pz orbitals and delocalized pi electrons whenever you see resonance structures being used. In this text, carboxylate groups will usually be drawn showing only one resonance contributor for the sake of simplicity, but you should always keep in mind that the two C-O bonds are equal, and that the negative charge is delocalized to both oxygens.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى) قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر مجموعة قصصية بعنوان (قلوب بلا مأوى)


















