


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 10-6-2019
Date: 28-12-2019
Date: 2-8-2020
|
The concept of pressure first developed in connection with studies relating to the atmosphere and vacuum that were first carried out in the 17th century
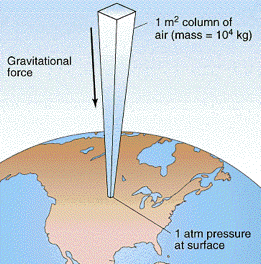
Figure 1.1: Origin of atmospheric pressure results from the combined force of all the air directly above an object.
The molecules of a gas are in a state of constant thermal motion, moving in straight lines until experiencing a collision that exchanges momentum between pairs of molecules and sends them bouncing off in other directions. This leads to a completely random distribution of the molecular velocities both in speed and direction— or it would in the absence of the Earth’s gravitational field which exerts a tiny downward force on each molecule, giving motions in that direction a very slight advantage. In an ordinary container this effect is too small to be noticeable, but in a very tall column of air the effect adds up: the molecules in each vertical layer experience more downward-directed hits from those above it. The resulting force is quickly randomized, resulting in an increased pressure in that layer which is then propagated downward into the layers below.
At sea level, the total mass of the sea of air pressing down on each 1-cm2 of surface is about 1034 g, or 10340 kg m–2. The force (weight) that the Earth’s gravitional acceleration g exerts on this mass is
f = ma = mg = (10340 kg)(9.81 m s–2) = 1.013 × 105 kg m s–2 = 1.013 × 105 newtons
resulting in a pressure of 1.013 × 105 n m–2 = 1.013 × 105 pa. The actual pressure at sea level varies with atmospheric conditions, so it is customary to define standard atmospheric pressure as 1 atm = 1.013 x 105 pa or 101 kpa. Although the standard atmosphere is not an SI unit, it is still widely employed. In meteorology, the bar, exactly 1.000 × 105 = 0.967 atm, is often used.
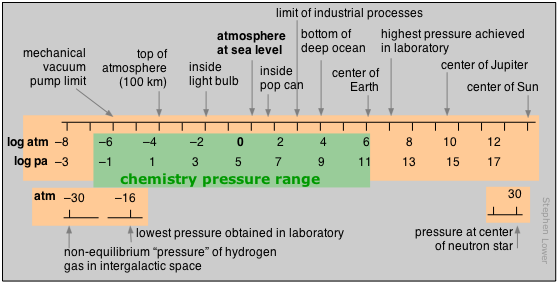
Figure 1.2: Pressure scales. Note that the numeric scale represents the logarithm of the number shown.



|
|
|
|
لصحة القلب والأمعاء.. 8 أطعمة لا غنى عنها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
حل سحري لخلايا البيروفسكايت الشمسية.. يرفع كفاءتها إلى 26%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تحتفي بذكرى ولادة الإمام محمد الجواد (عليه السلام)
|
|
|