
Structure and Isomerization
 المؤلف:
..................
المؤلف:
..................
 المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
LibreTexts Project
 الجزء والصفحة:
.................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
 19-6-2019
19-6-2019
 1265
1265
Structure and Isomerization
Two compounds that have the same formula and the same connectivity do not always have the same shape. There are two reasons why this may happen. In one case, the molecule may be flexible, so that it can twist into different shapes via rotation around individual sigma bonds. This phenomenon is called conformation, and it is covered in a different chapter. The second case occurs when two molecules appear to be connected the same way on paper, but are connected in two different ways in three dimensional space. These two, different molecules are called stereoisomers.
One simple example of stereoisomers from inorganic chemistry is diammine platinum dichloride, (NH3)2PtCl2. This important compound is sometimes called "platin" for short. As the formula implies, it contains a platinum ion that is coordinated to two ammonia ligands and two chloride ligands (remember, a ligand in inorganic chemistry is an electron donor that is attached to a metal atom, donating a pair of electrons to form a bond).
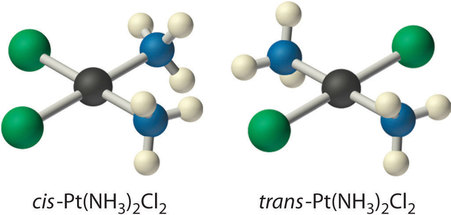
Figure 1.1 : Two stereoisomers. The atoms are connected to each other in the same order, but differ in their three-dimensional relationships. (left) The cis-Platin compound is square planar at platinum and is flat when viewed from the edge, and square when viewed from the face. (right) The trans-Platin compound is connected in the same way as in cis-platin, and is still square planar, but there is a different 3-dimensional arrangement
Platin is an example of a coordination compound. The way the different pieces of coordination compounds bond together is discussed in the chapter of Lewis acids and bases. For reasons arising from molecular orbital interactions, platin has a square planar geometry at the platinum atom. That arrangement results in two possible ways the ligands could be connected. The two sets of like ligands could be connected on the same side of the square or on opposite corners.
These two arrangements result in two different compounds; they are isomers that differ only in three-dimensional space.
- The one with the two amines beside each other is called cis-platin.
- These two ligands are 90 degrees from each other.
- The one with the amines across from each other is trans-platin.
- These two ligands are 180 degrees from each other.
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


