

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
The Domains of Chemistry
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
27-12-2019
1682
The Domains of Chemistry
Chemists study and describe the behavior of matter and energy in three different domains: macroscopic, microscopic, and symbolic. These domains provide different ways of considering and describing chemical behavior.
Macro is a Greek word that means “large.” The macroscopic domain is familiar to us: It is the realm of everyday things that are large enough to be sensed directly by human sight or touch. In daily life, this includes the food you eat and the breeze you feel on your face. The macroscopic domain includes everyday and laboratory chemistry, where we observe and measure physical and chemical properties, or changes such as density, solubility, and flammability.
The microscopic domain of chemistry is almost always visited in the imagination. Micro also comes from Greek and means “small.” Some aspects of the microscopic domains are visible through a microscope, such as a magnified image of graphite or bacteria. Viruses, for instance, are too small to be seen with the naked eye, but when we’re suffering from a cold, we’re reminded of how real they are.
However, most of the subjects in the microscopic domain of chemistry—such as atoms and molecules—are too small to be seen even with standard microscopes and often must be pictured in the mind. Other components of the microscopic domain include ions and electrons, protons and neutrons, and chemical bonds, each of which is far too small to see. This domain includes the individual metal atoms in a wire, the ions that compose a salt crystal, the changes in individual molecules that result in a color change, the conversion of nutrient molecules into tissue and energy, and the evolution of heat as bonds that hold atoms together are created.
The symbolic domain contains the specialized language used to represent components of the macroscopic and microscopic domains. Chemical symbols (such as those used in the periodic table), chemical formulas, and chemical equations are part of the symbolic domain, as are graphs and drawings. We can also consider calculations as part of the symbolic domain. These symbols play an important role in chemistry because they help interpret the behavior of the macroscopic domain in terms of the components of the microscopic domain. One of the challenges for students learning chemistry is recognizing that the same symbols can represent different things in the macroscopic and microscopic domains, and one of the features that makes chemistry fascinating is the use of a domain that must be imagined to explain behavior in a domain that can be observed.
A helpful way to understand the three domains is via the essential and ubiquitous substance of water. That water is a liquid at moderate temperatures, will freeze to form a solid at lower temperatures, and boil to form a gas at higher temperatures (Figure 1.1.4) are macroscopic observations. But some properties of water fall into the microscopic domain—what we cannot observe with the naked eye. The description of water as comprised of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, and the explanation of freezing and boiling in terms of attractions between these molecules, is within the microscopic arena. The formula H2O, which can describe water at either the macroscopic or microscopic levels, is an example of the symbolic domain. The abbreviations (g) for gas, (s) for solid, and (l) for liquid are also symbolic.
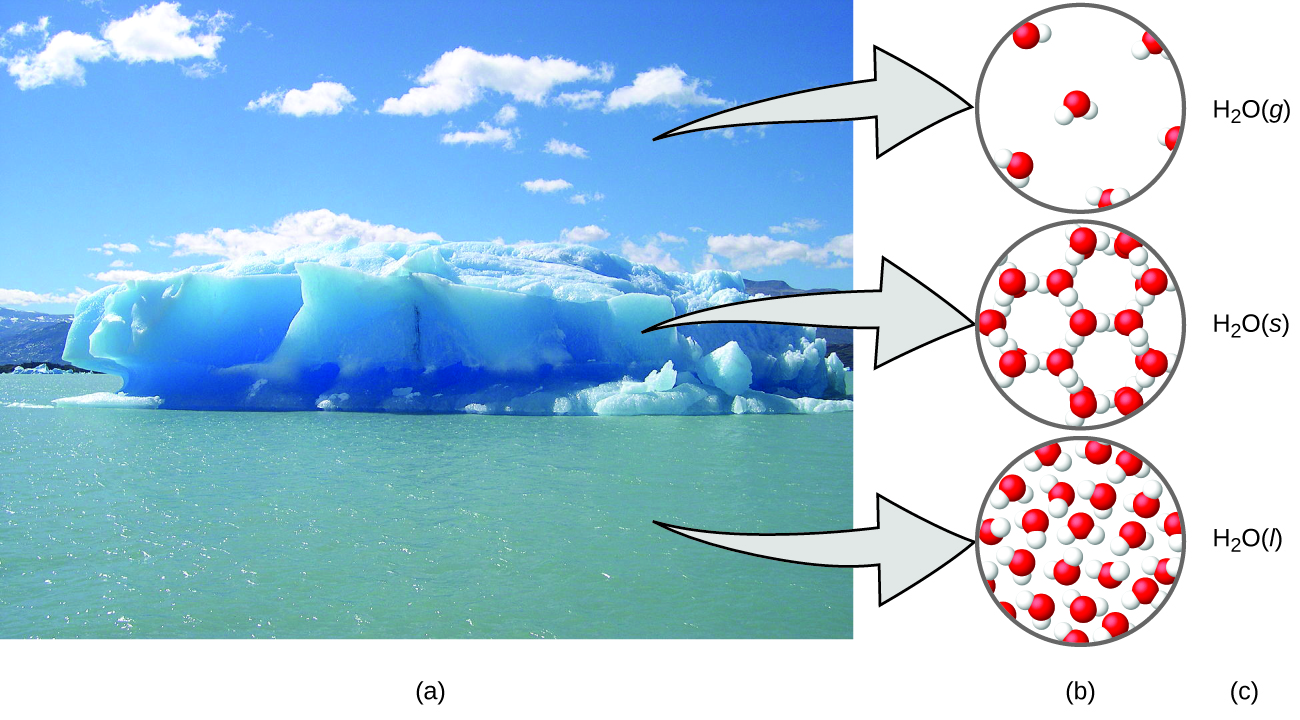
Figure 1.1 : (a) Moisture in the air, icebergs, and the ocean represent water in the macroscopic domain. (b) At the molecular level (microscopic domain), gas molecules are far apart and disorganized, solid water molecules are close together and organized, and liquid molecules are close together and disorganized. (c) The formula H2O symbolizes water, and (g), (s), and (l) symbolize its phases. Note that clouds are actually comprised of either very small liquid water droplets or solid water crystals; gaseous water in our atmosphere is not visible to the naked eye, although it may be sensed as humidity. (credit a: modification of work by “Gorkaazk”/Wikimedia Commons).
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء عامة
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء عامة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















