


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 1-9-2019
Date: 26-1-2016
Date: 21-8-2016
|
Regiochemistry deals with where the substituent bonds on the product. Zaitsev's and Markovnikov's rules address regiochemistry, but Zaitsev's rule applies when synthesizing an alkene while Markovnikov's rule describes where the substituent bonds onto the product. In the case of electrophilic hydration, Markovnikov's rule is the only rule that directly applies. See the following for an in-depth explanation of regiochemistry Markovnikov explanation: Radical Additions--Anti-Markovnikov Product Formation
In the mechanism for a 3º alcohol shown above, the red H is added to the least-substituted carbon connected to the nucleophilic double bonds (it has less carbons attached to it). This means that the carbocation forms on the 3º carbon, causing it to be highly stabilized by hyperconjugation—electrons in nearby sigma (single) bonds help fill the empty p-orbital of the carbocation, which lessens the positive charge. More substitution on a carbon means more sigma bonds are available to "help out" (by using overlap) with the positive charge, which creates greater carbocation stability. In other words, carbocations form on the most substituted carbon connected to the double bond. Carbocations are also stabilized by resonance, but resonance is not a large factor in this case because any carbon-carbon double bonds are used to initiate the reaction, and other double bonded molecules can cause a completely different reaction.
If the carbocation does originally form on the less substituted part of the alkene, carbocation rearrangements occur to form more substituted products:
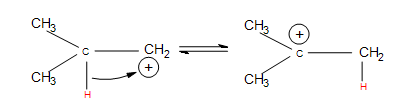
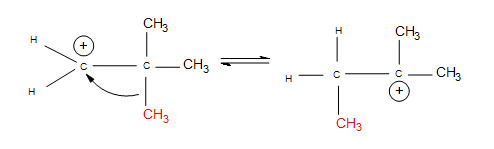
The nucleophile attacks the positive charge formed on the most substituted carbon connected to the double bond, because the nucleophile is seeking that positive charge. In the mechanism for a 3º alcohol shown above, water is the nucleophile. When the green H is removed from the water molecule, the alcohol attached to the most substituted carbon. Hence, electrophilic hydration follows Markovnikov's rule.



|
|
|
|
لصحة القلب والأمعاء.. 8 أطعمة لا غنى عنها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
حل سحري لخلايا البيروفسكايت الشمسية.. يرفع كفاءتها إلى 26%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تحتفي بذكرى ولادة الإمام محمد الجواد (عليه السلام)
|
|
|