


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 25-7-2020
Date: 27-4-2019
Date: 24-1-2018
|
Ever since the discovery early in the 19th century that solutions of salts and other electrolytes conduct electric current, there has been general agreement that the forces that hold atoms together must be electrical in nature. Electrolytic solutions contain ions having opposite electrical charges, opposite charges attract, so perhaps the substances from which these ions come consist of positive and negatively charged atoms held together by electrostatic attraction.
It turns out that this is not true generally, but a model built on this assumption does a fairly good job of explaining a rather small but important class of compounds that are called ionic solids. The most well known example of such a compound is sodium chloride, which consists of two interpenetrating lattices of Na+ and Cl– ions arranged in such as way that every ion of one type is surrounded (in three dimensional space) by six ions of opposite charge.
The main limitation of this model is that it applies really well only to the small class of solids composed of Group 1 and 2 elements with highly electronegative elements such as the halogens. Although compounds such as CuCl2 dissociate into ions when they dissolve in water, the fundamental units making up the solid are more like polymeric chains of covalently-bound CuCl2 molecules that have little ionic character.
According to the ionic electrostatic model, solids such as NaCl consist of positive and negative ions arranged in a crystal lattice. Each ion is attracted to neighboring ions of opposite charge, and is repelled by ions of like charge; this combination of attractions and repulsions, acting in all directions, causes the ion to be tightly fixed in its own location in the crystal lattice.
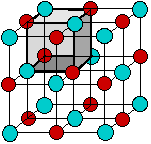
Since electrostatic forces are nondirectional, the structure of an ionic solid is determined purely by geometry: two kinds of ions, each with its own radius, will fall into whatever repeating pattern will achieve the lowest possible potential energy. Surprisingly, there are only a small number of possible structures



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|