

علم الكيمياء

تاريخ الكيمياء والعلماء المشاهير

التحاضير والتجارب الكيميائية

المخاطر والوقاية في الكيمياء

اخرى

مقالات متنوعة في علم الكيمياء

كيمياء عامة


الكيمياء التحليلية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء التحليلية

التحليل النوعي والكمي

التحليل الآلي (الطيفي)

طرق الفصل والتنقية


الكيمياء الحياتية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الحياتية

الكاربوهيدرات

الاحماض الامينية والبروتينات

الانزيمات

الدهون

الاحماض النووية

الفيتامينات والمرافقات الانزيمية

الهرمونات


الكيمياء العضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء العضوية

الهايدروكاربونات

المركبات الوسطية وميكانيكيات التفاعلات العضوية

التشخيص العضوي

تجارب وتفاعلات في الكيمياء العضوية


الكيمياء الفيزيائية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الفيزيائية

الكيمياء الحرارية

حركية التفاعلات الكيميائية

الكيمياء الكهربائية


الكيمياء اللاعضوية

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء اللاعضوية

الجدول الدوري وخواص العناصر

نظريات التآصر الكيميائي

كيمياء العناصر الانتقالية ومركباتها المعقدة


مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء

كيمياء النانو

الكيمياء السريرية

الكيمياء الطبية والدوائية

كيمياء الاغذية والنواتج الطبيعية

الكيمياء الجنائية


الكيمياء الصناعية

البترو كيمياويات

الكيمياء الخضراء

كيمياء البيئة

كيمياء البوليمرات

مواضيع عامة في الكيمياء الصناعية

الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
Interpreting Chemical Equations
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المصدر:
................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
12-8-2020
1548
Interpreting Chemical Equations
The mole, as you remember, is a quantitative measure that is equivalent to Avogadro's number of particles. So how does this relate to the chemical equation? Look at the chemical equation below.

The coefficients used, as we have learned, tell us the relative amounts of each substance in the equation. So for every 2 units of copper (II) sulfate (CuSO4) we have, we need to have 4 units of potassium iodide (KI). For every two dozen copper (II) sulfates, we need 4 dozen potassium iodides. Because the unit "mole" is also a counting unit, we can interpret this equation in terms of moles, as well: For every two moles of copper (II) sulfate, we need 4 moles potassium iodide.
The production of ammonia (NH3) from nitrogen and hydrogen gases is an important industrial reaction called the Haber process, after German chemist Fritz Haber.
The balanced equation can be analyzed in several ways, as shown in the figure below.
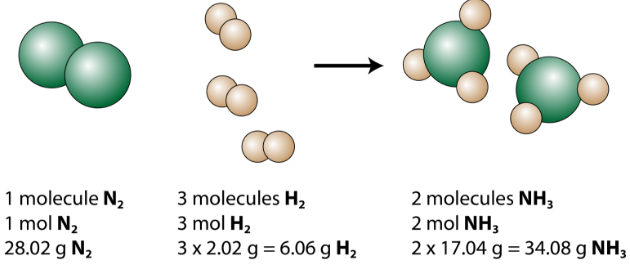
Figure 1 : This representation of the production of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen show several ways to interpret the quantitative information of a chemical reaction.
We see that 1 molecule of nitrogen reacts with 3 molecules of hydrogen to form 2 molecules of ammonia. This is the smallest possible relative amounts of the reactants and products. To consider larger relative amounts, each coefficient can be multiplied by the same number. For example, 10 molecules of nitrogen would react with 30 molecules of hydrogen to produce 20 molecules of ammonia.
The most useful quantity for counting particles is the mole. So if each coefficient is multiplied by a mole, the balanced chemical equation tells us that 1 mole of nitrogen reacts with 3 moles of hydrogen to produce 2 moles of ammonia. This is the conventional way to interpret any balanced chemical equation.
Finally, if each mole quantity is converted to grams by using the molar mass, we can see that the law of conservation of mass is followed. 1mol of nitrogen has a mass of 28.02g, while 3mol of hydrogen has a mass of 6.06g, and 2mol of ammonia has a mass of 34.08g.
Mass and the number of atoms must be conserved in any chemical reaction. The number of molecules is not necessarily conserved.
 الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء عامة
الاكثر قراءة في كيمياء عامة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















