
Ionizing vs. Nonionizing Radiation
 المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
المؤلف:
LibreTexts Project
 المصدر:
................
المصدر:
................
 الجزء والصفحة:
.................
الجزء والصفحة:
.................
 3-9-2020
3-9-2020
 1832
1832
Ionizing vs. Nonionizing Radiation
There is a large difference in the magnitude of the biological effects of nonionizing radiation (for example, light and microwaves) and ionizing radiation, emissions energetic enough to knock electrons out of molecules (for example, α and β particles, γ rays, X-rays, and high-energy ultraviolet radiation) (Figure 1 ).
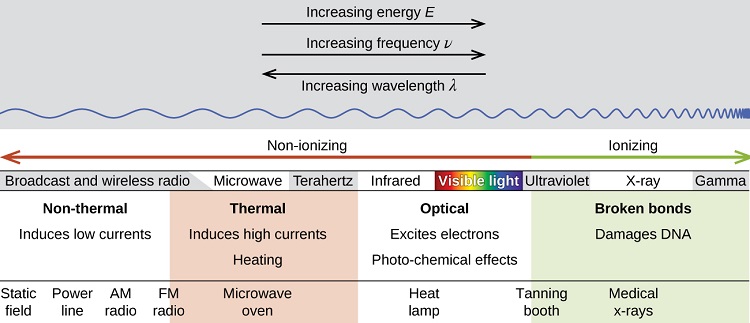
Figure 1 : Lower frequency, lower-energy electromagnetic radiation is nonionizing, and higher frequency, higher-energy electromagnetic radiation is ionizing.
Energy absorbed from nonionizing radiation speeds up the movement of atoms and molecules, which is equivalent to heating the sample. Although biological systems are sensitive to heat (as we might know from touching a hot stove or spending a day at the beach in the sun), a large amount of nonionizing radiation is necessary before dangerous levels are reached. Ionizing radiation, however, may cause much more severe damage by breaking bonds or removing electrons in biological molecules, disrupting their structure and function. The damage can also be done indirectly, by first ionizing H2O (the most abundant molecule in living organisms), which forms a H2O+ ion that reacts with water, forming a hydronium ion and a hydroxyl radical:
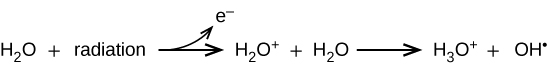
Figure 2.
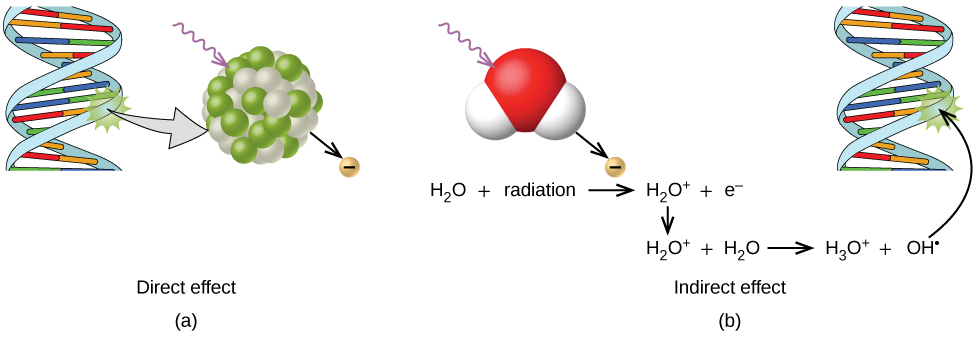
Figure 2 : Ionizing radiation can (a) directly damage a biomolecule by ionizing it or breaking its bonds, or (b) create an H2O+ ion, which reacts with H2O to form a hydroxyl radical, which in turn reacts with the biomolecule, causing damage indirectly.
 الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
الاكثر قراءة في الكيمياء الاشعاعية والنووية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


