One of the largest and most diverse classes of reactions is composed of nucleophilic additions to a carbonyl group. Conjugation of a double bond to a carbonyl group transmits the electrophilic character of the carbonyl carbon to the beta-carbon of the double bond. These conjugated carbonyl are called enones or α, β unsaturated carbonyls. A resonance description of this transmission is shown below.

From this formula it should be clear that nucleophiles may attack either at the carbonyl carbon, as for any aldehyde, ketone or carboxylic acid derivative, or at the beta-carbon. These two modes of reaction are referred to as 1,2-addition and 1,4-addition respectively. A 1,4-addition is also called a conjugate addition.
Basic reaction of 1,2 addition
Here the nucleophile adds to the carbon which is in the one position. The hydrogen adds to the oxygen which is in the two position.

Basic reaction of 1,4 addition
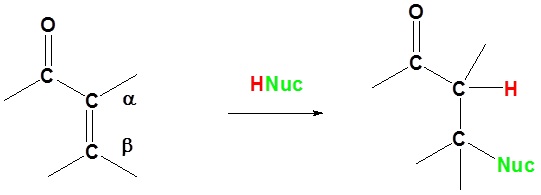
In 1,4 addition the nucleophile is added to the carbon β to the carbonyl while the hydrogen is added to the carbon α to the carbonyl.
Mechanism for 1,4 addition
1) Nucleophilic attack on the carbon β to the carbonyl

2) Proton Transfer

Here we can see why this addition is called 1,4. The nucleophile bonds to the carbon in the one position and the hydrogen adds to the oxygen in the four position.
3) Tautomerization

Going from reactant to products simplified