


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 14-10-2020
Date: 10-10-2020
Date: 24-10-2020
|
ULTRAVIOLET
As the wavelength of an EM disturbance becomes shorter than the smallest we can see, the energy contained in each individual photon increases. The UV range of wavelengths starts at about 390 nm and extends down to about 1 nm. At a wavelength of approximately 290 nm, the atmosphere becomes highly absorptive, and at wavelengths shorter than this, the air is essentially opaque. This protects the environment against damaging ultraviolet radiation from the Sun. Ozone (molecules consisting of three oxygen atoms) in the upper atmosphere is primarily responsible for this effect. Ozone pollution, prevalent in large cities during the summer months, further attenuates UV. Ordinary glass is virtually opaque at UV, so cameras with glass lenses cannot be used to take photographs in this part of the spectrum. Instead, a pinhole-type device is used, and this severely limits the amount of energy that passes into the detector. While a camera lens has a diameter of several millimeters or centimeters, a pinhole is less than a millimeter across.
Another type of device that can be used to sense UV and to measure its intensity at various wavelengths is the spectrophotometer. A diffraction grating is used to disperse EM energy into its constituent wavelengths from IR through the visible and into the UV range. By moving the sensing device back and forth, any desired wavelength can be singled out for analysis.
The principle of operation of the spectrophotometer is shown Fig. 1. At the extremely short-wavelength end of the UV spectrum (hard UV), radiation counters are sometimes used, similar to the apparatus employed for the detection of x-rays and gamma rays. For photographic purposes, ordinary camera film will work at the longer UV wavelengths (soft UV). A special film, rather like x-ray film, is necessary to make hard-UV photos.
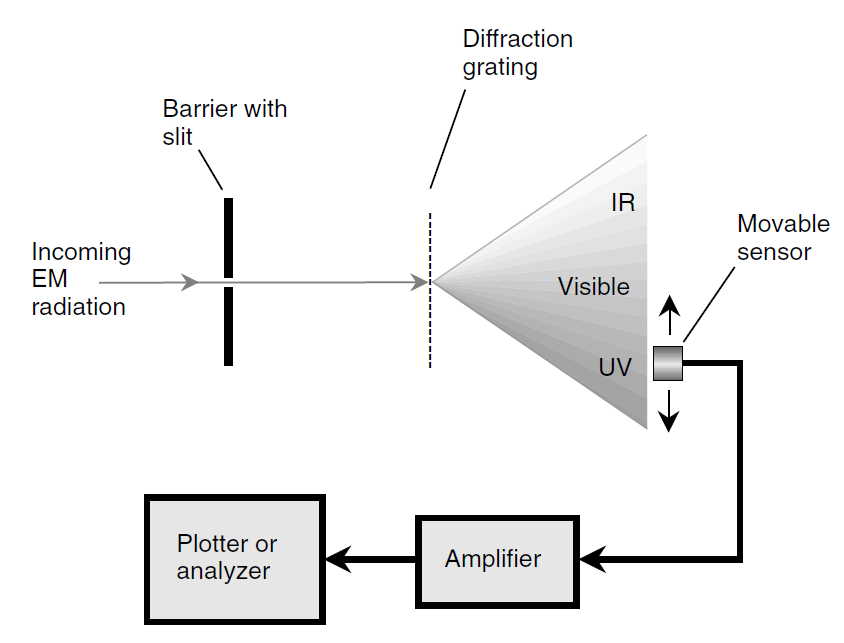
Fig. 1. Functional diagram of a spectrophotometer, which can be used to sense and measure EM radiation at IR, visible, and UV wavelengths.
UV rays possess an interesting property that can be observed using a so-called black light. Most hobby shops sell lamps of this sort. They are cylindrical in shape, and superficially, they can be mistaken for small fluorescent tubes. (The incandescent black light bulbs sold in department stores are not especially good sources of UV.) When subjected to UV, certain substances glow brightly in the visible range. This is known as fluorescence. Art stores sell acrylic paints that are specially tailored to glow in various colors when UV strikes them. The effect in a darkened room can be striking. The phosphor coatings on CRTs fluoresce under UV too. So will certain living organisms, such as scorpions. If you live in the desert, go outside some night with a black light and switch it on. If there are scorpions around, you’ll find out.
Most of the radiation from the Sun occurs in the IR and visible parts of the EM spectrum. If the Sun were a much hotter star, producing more energy in the UV range, life on any earthlike planet in its system would have developed in a different way, if at all. Excessive exposure to UV, even in the relatively small amounts that reach the Earth’s surface on bright days, can, over time, cause skin cancer and eye cataracts. There is evidence to suggest that excessive exposure to UV suppresses the activity of the immune system, rendering people and animals more susceptible to infectious diseases. Some scientists believe that the ozone hole in the upper atmosphere, prevalent in the southern hemisphere, is growing because of increased production and emission of certain chemicals by humankind. If this is the case, and if the problem worsens, we should expect that it will affect the evolution of life on this planet.



|
|
|
|
دراسة: حفنة من الجوز يوميا تحميك من سرطان القولون
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
تنشيط أول مفاعل ملح منصهر يستعمل الثوريوم في العالم.. سباق "الأرنب والسلحفاة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
الطلبة المشاركون: مسابقة فنِّ الخطابة تمثل فرصة للتنافس الإبداعي وتنمية المهارات
|
|
|