
Application of Kirchoff’s Law
 المؤلف:
E. R. Huggins
المؤلف:
E. R. Huggins
 المصدر:
Physics 2000
المصدر:
Physics 2000
 الجزء والصفحة:
665
الجزء والصفحة:
665
 19-12-2020
19-12-2020
 2056
2056
Application of Kirchoff’s Law
There are some relatively standard, cookbook like procedures that make it easy to apply Kirchoff’s law to the analysis of circuits. The steps in the recipe are as follows:
(1) Sketch the circuit and use arrows to show the direction of the positive current in each loop as we did in Figure (1). Do not be too concerned about getting the correct direction for the current i. If you have the
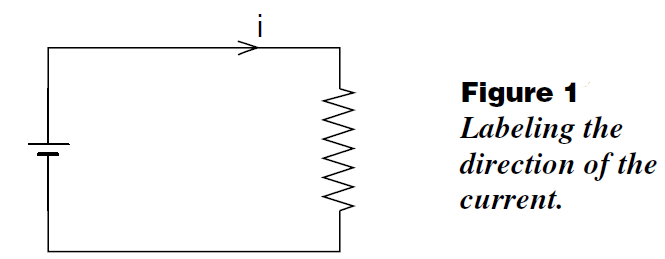
arrow pointing the wrong way, then when you finish solving the problem, i will turn out to be negative.
(2) Label all the voltage rises in the circuit. Use arrows to indicate the direction of the voltage rise as we did in Figure (2). Note that if we go through the resistor in the direction of the current, we get a voltage drop. Therefore the arrow showing the voltage rise in a resistor must point back, opposite to the direction of the

current i in the resistor. (The analogy is to a rock strewn waterfall where the water loses hydrodynamic voltage as it flows down through the rocks. The direction of the voltage rise is back up the waterfall, in a direction opposite to that of the current.)
(3) The final step is to “walk” around the loop in the direction of i (or any direction you choose), and set the sum of the voltage rises you encounter equal to zero. If you encounter an arrow that points in the direction you are walking, it counts as a positive voltage rise (like Vb in Figure 2). If the arrow points against you (like VR ), then it is a negative rise. Applying this rule to Figure (2) gives
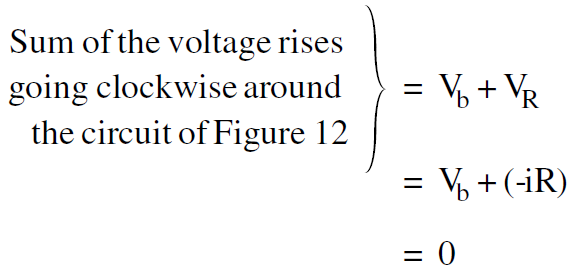 ........(1)
........(1)
Equation (1) gives
i = Vb/R
 الاكثر قراءة في الكهربائية
الاكثر قراءة في الكهربائية
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


