


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 21-3-2016
Date: 21-3-2016
Date: 10-11-2020
|
Negative Image Distance
The lens equation is more general than you might expect, for it works equally well for positive and negative distances and focal lengths. Let us start by seeing what we mean by a negative image distance.
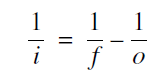 (1)
(1)
let us see what happens if 1/o is bigger than 1/f so that i turns out to be negative. If 1/o is bigger than 1/f, that means that o is less than f and we have placed the object within the focal length as shown in Figure (1). When we trace out two rays from the tip of the image, we find that the rays diverge after they pass through the lens. They diverge as if they were coming from a point behind the object, a point shown by the dotted lines. In this case we have what is called a virtual image, which is located at a negative image distance (i). This negative image distance is correctly given by the lens equation (1).
(We will not drag you through another geometrical proof of the lens equation for negative image distances. It should be fairly convincing that just when the image distance becomes negative in the lens equation, the geometry shows that we switch from a real image on the right side of the lens to a virtual image on the left.)

Figure 1: When the object is located within the focal length, we get a virtual image behind the object



|
|
|
|
دراسة تحدد أفضل 4 وجبات صحية.. وأخطرها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تحتفي بذكرى ولادة الإمام محمد الجواد (عليه السلام)
|
|
|