

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Genes Show a Wide Distribution of Sizes Due Primarily to Intron Size and Number Variation
المؤلف:
JOCELYN E. KREBS, ELLIOTT S. GOLDSTEIN and STEPHEN T. KILPATRICK
المصدر:
LEWIN’S GENES XII
الجزء والصفحة:
9-3-2021
2166
Genes Show a Wide Distribution of Sizes Due Primarily to Intron Size and Number Variation
KEY CONCEPTS
-Most genes are uninterrupted in Saccharomyces cerevisiae but are interrupted in multicellular eukaryotes.
-Exons are usually short, typically encoding fewer than 100 amino acids.
-Introns are short in unicellular/oligocellular eukaryotes but can be many kb in multicellular eukaryotes.
-The overall length of a gene is determined largely by its introns.
FIGURE 1. compares the organization of genes in a yeast, an insect, and mammals. In the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the majority of genes (more than 96%) are uninterrupted, and those that have exons generally have three or fewer. There are virtually no S. cerevisiae genes with more than four exons.
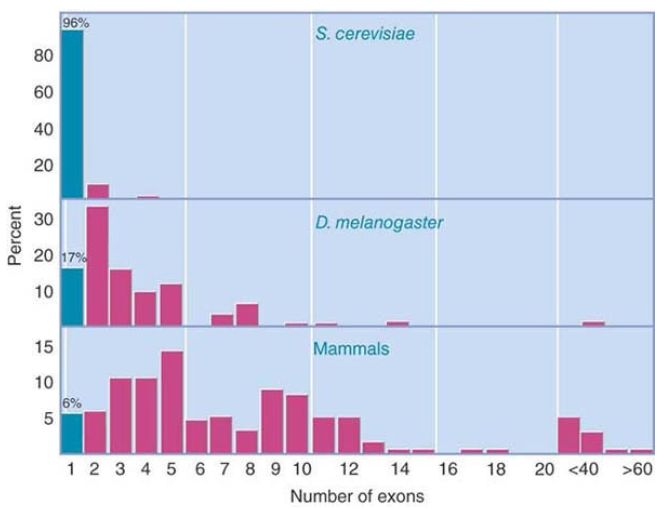
FIGURE 1. Most genes are uninterrupted in yeast, but most genes are interrupted in flies and mammals. (Uninterrupted genes have only one exon and are totaled in the leftmost column in blue.)
In insects and mammals, the situation is reversed. Only a few genes have uninterrupted coding sequences (6% in mammals). Insect genes tend to have a small number of exons, typically fewer than 10. Mammalian genes are split into more pieces and some have more than 60 exons. Approximately 50% of mammalian genes have more than 10 introns. If we examine the effect of intron number variation on the total size of genes, we see in FIGURE 2. that there is a striking difference between yeast and multicellular eukaryotes. The average yeast gene is 1.4 kb long, and very few are longer than 5 kb. The predominance of interrupted genes in multicellular eukaryotes, however, means that the gene can be much larger than the sum total of the exon lengths. Only a small percentage of genes in flies or mammals are shorter than 2 kb, and most have lengths between 5 kb and 100 kb. The average human gene is 27 kb long. The gene encoding Caspr2, with a length of 2,300 kb, is the longest known human gene (it encompasses nearly 1.5% of the entire length of human chromosome 7!).
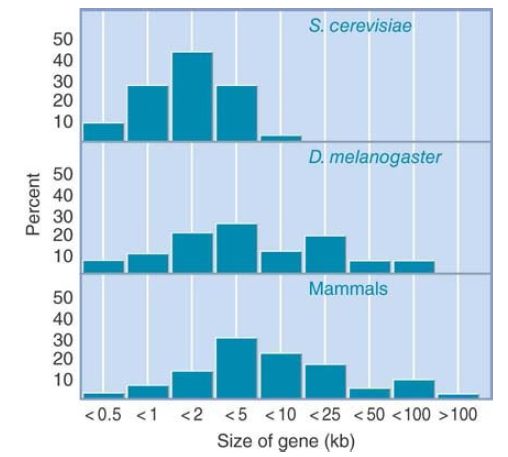
FIGURE 2. Yeast genes are short, but genes in flies and mammals have a dispersed bimodal distribution extending to very long sizes.
The switch from largely uninterrupted to largely interrupted genes seems to have occurred with the evolution of multicellular eukaryotes. In fungi other than S. cerevisiae, the majority of genes are interrupted, but they have a relatively small number of exons (fewer than 6) and are fairly short (less than 5 kb). In the fruit fly, gene sizes have a bimodal distribution—many are short but some are quite long. With this increase in the length of the gene due to the increased number of introns, the correlation between genome size and organism complexity becomes weak. FIGURE 3.9 shows that exons encoding stretches of protein tend to be fairly small. In multicellular eukaryotes, the average exon codes for about 50 amino acids, and the general distribution is consistent with the hypothesis that genes have evolved by the gradual addition of exon units that encode short, functionally independent protein domains (see the Genome Sequences and Evolution chapter). There is no significant difference in the average size of exons in different multicellular eukaryotes, although the size range is smaller in vertebrates for which there are few exons longer than 200 bp. In yeast, there are some longer exons that represent uninterrupted genes for which the coding sequence is intact. There is a tendency for exons containing untranslated 5′ and 3′ regions to be longer than those that encode proteins.
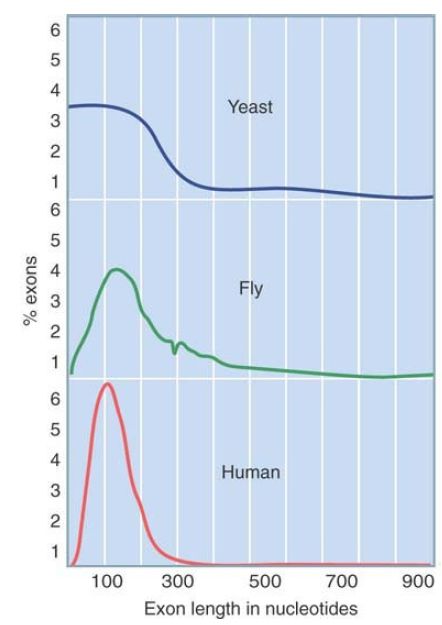
FIGURE 3. Exons encoding polypeptides are usually short.
FIGURE 4 shows that introns vary widely in size among multicellular eukaryotes. (Note that the scale of the x-axis differs from that of Figure 3.) In worms and flies, the average intron is no longer than the exons. There are no very long introns in worms, but flies contain many. In vertebrates, the size distribution is much wider, extending from approximately the same length as the exons (less than 200 bp) up to 60 kb in extreme cases. (Some fish, such as fugu [pufferfish], have compressed genomes with shorter introns and intergenic regions than mammals have.)
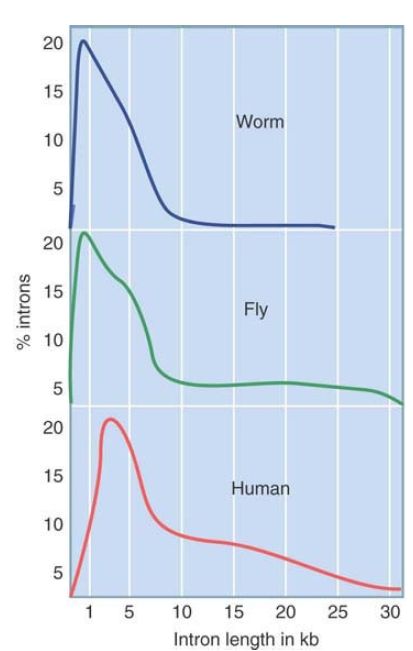
FIGURE 4. Introns range from very short to very long.
Very long genes are the result of very long introns, not the result of encoding longer products. There is no correlation between total gene size and total exon size in multicellular eukaryotes, nor is there a good correlation between gene size and number of exons. The size of a gene is therefore determined primarily by the lengths of its individual introns. In mammals and insects, the “average” gene is approximately 5 times that of the total length of its exons.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















