
THE COMPTON EFFECT
 المؤلف:
Shabnam Siddiqui
المؤلف:
Shabnam Siddiqui
 المصدر:
Quantum Mechanics
المصدر:
Quantum Mechanics
 الجزء والصفحة:
14
الجزء والصفحة:
14
 21-3-2021
21-3-2021
 2052
2052
THE COMPTON EFFECT
The Compton effect was observed in 1923 by Arthur Holly Compton. He demonstrated another experimental observation toward the validation of the particle nature of light. The experiment consisted of directing radiation of high frequency such as X-rays on free electrons. The interaction between the X-rays and the free electrons lead to deflection of the X-rays with reduced frequency.
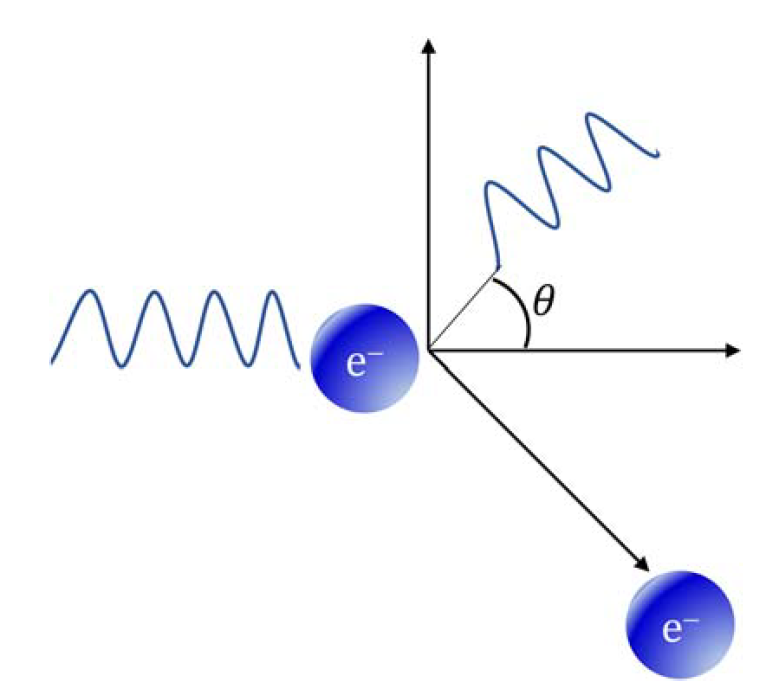
FIGURE 1: A schematic of electron scattering by X-rays.
Also, the interaction caused the electrons to recoil so that the electron seemed to be deflected in the same manner as if they had undergone collision with another particle. This phenomenon can be simply explained using the particle nature of light. An X-ray is comprised of X-ray photons, and each photon has energy, Ephoton = hν and they also carry momentum as shown:
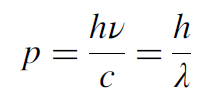
The previous relationship is called De Broglie’s momentum relationship for the matter waves associated with a material particle which will be discussed in details in the next chapter. Here p is the momentum carried by X-rays photon, and is the wavelength of the X-rays. Thus, the interaction between X-rays and free electrons can be viewed as a collision between X-ray photons (particles) and electrons, just in the same manner as an elastic collision between two billiard balls. The application of mechanical laws of conservation of momentum and energy lead to the establishment of the following relationship:
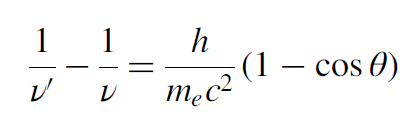 ........(2)
........(2)
where ν ′ = the frequency of the deflected photon after collision, ν = the frequency of the incident photon, θ = the angle of deflection, me = the mass of an electron, and h = Planck’s constant. According to the previous equation, the loss in momentum of the incident X-ray photon during collision results in the emergence of a new X-ray photon of frequency ν ′ that is deflected at an angle θ with an incident photon. It also causes the stationary electron to gain momentum and rebound. The Compton effect further established the foundation of the particle nature of all types of radiation (Figure 1).
 الاكثر قراءة في ميكانيكا الكم
الاكثر قراءة في ميكانيكا الكم
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


