
Electrons
 المؤلف:
Stan Gibilisco
المؤلف:
Stan Gibilisco
 المصدر:
Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics
المصدر:
Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics
 الجزء والصفحة:
5
الجزء والصفحة:
5
 29-3-2021
29-3-2021
 2397
2397
Electrons
Surrounding the nucleus of an atom are particles having opposite electric charge from the protons. These are the electrons. Physicists arbitrarily call the electrons’ charge negative, and the protons’ charge positive. An electron has exactly the same charge quantity as a proton, but with opposite polarity. The charge on a single electron or proton is the smallest possible electric charge. All charges, no matter how great, are multiples of this unit charge.
One of the earliest ideas about the atom pictured the electrons embedded in the nucleus, like raisins in a cake. Later, the electrons were seen as orbiting the nucleus, making the atom like a miniature solar system with the electrons as the planets (Fig. 1).
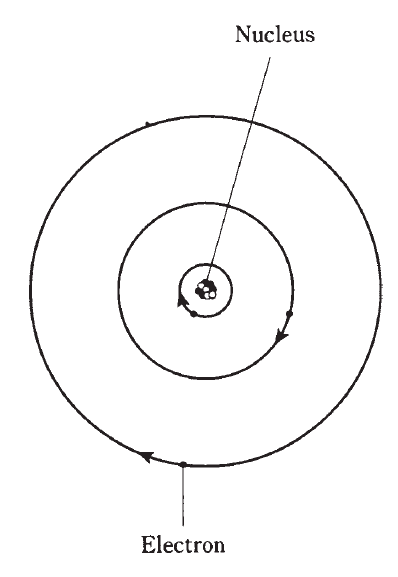
Fig 1: An early model of the atom, developed about the year 1900, rendered electrons like planets and the nucleus like the sun in a miniature solar system. Electric charge attraction kept the electrons from flying away.
Still later, this view was modified further. Today, the electrons are seen as so fastmoving, with patterns so complex, that it is not even possible to pinpoint them at any given instant of time. All that can be done is to say that an electron will just as likely be inside a certain sphere as outside. These spheres are known as electron shells. Their centers correspond to the position of the atomic nucleus. The farther away from the nucleus the shell, the more energy the electron has (Fig. 2).
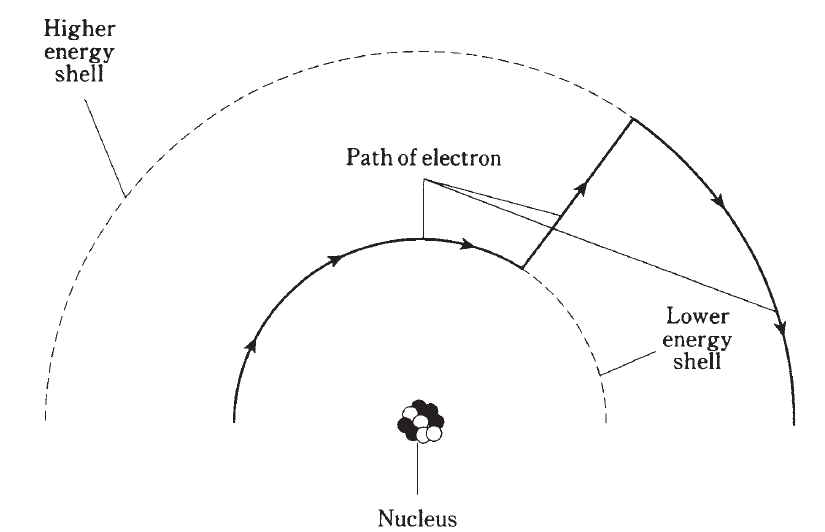
Fig. 2: Electrons move around the nucleus of an atom at defined levels corresponding to different energy states. This is a simplified drawing, depicting an electron gaining energy.
Electrons can move rather easily from one atom to another in some materials. In other substances, it is difficult to get electrons to move. But in any case, it is far easier to move electrons than it is to move protons. Electricity almost always results, in some way, from the motion of electrons in a material.
Electrons are much lighter than protons or neutrons. In fact, compared to the nucleus of an atom, the electrons weigh practically nothing. Generally, the number of electrons in an atom is the same as the number of protons.
The negative charges therefore exactly cancel out the positive ones, and the atom is electrically neutral. But under some conditions, there can be an excess or shortage of electrons. High levels of radiant energy, extreme heat, or the presence of an electric field (discussed later) can “knock” or “throw” electrons loose from atoms, upsetting the balance.
 الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
الاكثر قراءة في الألكترونيات
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


