


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 5-11-2015
Date: 1-8-2021
Date: 5-11-2015
|
Muscular System
Muscles of the human body comprise three types: cardiac, smooth, and skeletal(Fig. 1 ). Cardiac muscle forms the walls of the heart. Cardiac muscle cells are striated but smaller than skeletal muscle cells and have a single nucleus per cell. Smooth muscle is primarily found in the walls of hallow viscera and blood vessels. Smooth muscle cells lack striations, have one nucleus per cell, and are small and narrow in appearance.
The gross Skeletal muscle cells are striated and converge to form skeletal muscles of varied shapes and sizes (Fig 2). As shown in Table 1., skeletal muscles can be described according to their shape. A skeletal muscle (e.g., biceps brachii muscle) consists of numerous fascicles, which consist of numerous skeletal muscle cells (also called skeletal muscle fibers). A skeletal muscle cell, in turn, consists of numerous myofibrils comprising thick and thin myofilaments (Fig. 3).
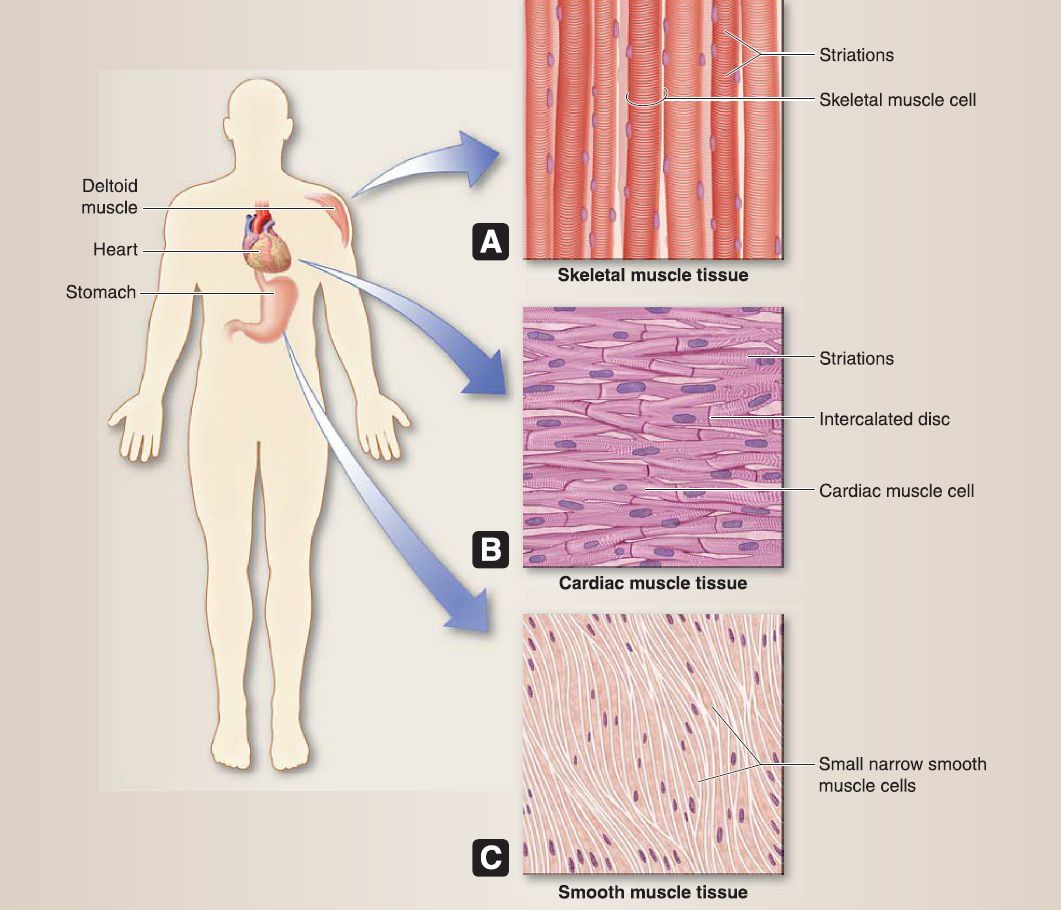
Figure 1: Muscle tissue. A, Skeletal muscle. B, Cardiac muscle. C, Smooth muscle.
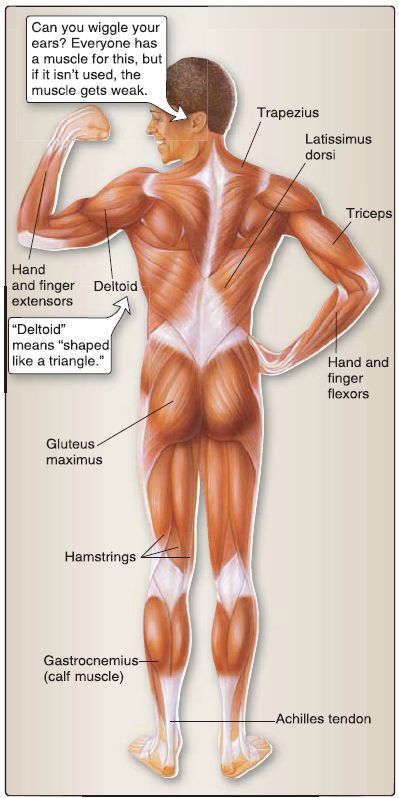
Figure 2: Skeletal muscles.

Figure 3 : Skeletal muscle organization.
Table 1: Muscle Shapes

A. Connective tissue components
The connective tissue components of skeletal muscle transmit the contractile force generated by the skeletal muscle cell to the tendon and bone so that movement of the joint occurs. The connective tissue components include the epimysium, a dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the entire skeletal muscle; the perimysium, a dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds a bundle of skeletal muscle cells (fascicle); and the endomysium, a delicate loose connective tissue that surrounds an individual skeletal muscle cell (see Fig. 3).
B. Skeletal muscle cell
The skeletal muscle cell is cylinder shaped with tapered ends and is ~2-100 mm in length and 10-100 μm in diameter. It is multinucleated with thin, flat nuclei located at the periphery of the cell. As shown in Figure 4, its cytoplasm is characterized by striations that consist of the A band (dark), I band (light), and the Z disc. The three types of skeletal muscle cells include type I (red), type Ila (intermediate), and type llb (white). High-endurance athletes (e.g., marathon runners) have a high percentage of type I skeletal muscle cells, and low-endurance athletes (e.g., sprinters, weightlifters) have a high percentage of type llb skeletal muscle cells. Type Ila have characteristic of both types I and llb skeletal muscle cells.
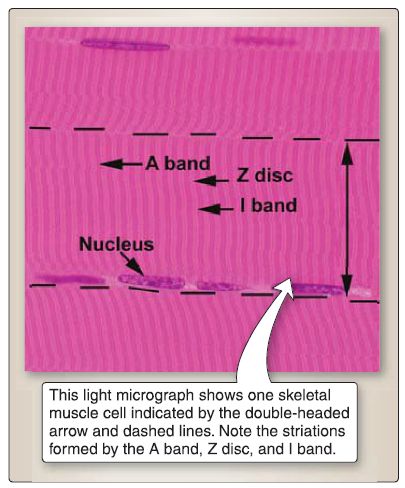
Figure 4: Skeletal muscle cell.
C. Neuromuscular junction
The neuromuscular junction is the junctional relationship of an a-motoneuron and a skeletal muscle cell in which the a-motoneuron transmits a signal to the skeletal muscle cell, thereby causing contraction of the muscle (Fig. 5). The axons of a-motoneurons whose cell bodies are located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord innervate skeletal muscle cells. The axons end as synaptic terminals with synaptic vesicles that contain the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh). ACh binds to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), which is a transmitter-gated ion channel located on the skeletal muscle cell. When ACh binds to nAChR, a "gate" opens and allows Na+ influx into the skeletal muscle cell, causing depolarization.
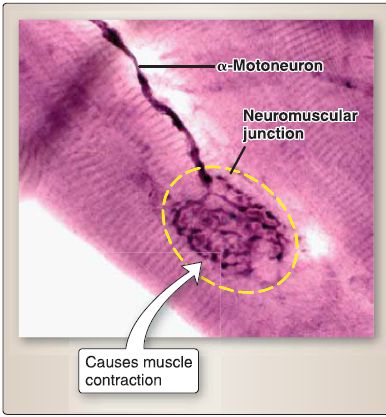
Figure 5 : Neuromuscular junction.
D. Motor unit
A single axon of an a-motoneuron may innervate 1 to 5 skeletal muscle cells, which forms a small motor unit. Or, a single axon of an a-motoneuron may branch and innervate more than 150 skeletal muscle cells, forming a large motor unit.
A motor unit is the functional contractile unit of a gross skeletal muscle, not a skeletal muscle cell.
E. Muscle spindle
As shown in Figure 6, the muscle spindle is a small, elongated, encapsulated structure distributed throughout a gross skeletal muscle that senses both dynamic changes in muscle length and static muscle length as well as activating the myotactic (stretch) reflex (e.g., knee jerk reflex). It consists of nuclear bag cells and nuclear chain cells and is innervated by type la sensory neurons (annulospiral endings), type II sensory neurons (flower-spray endings), and y-motoneurons.
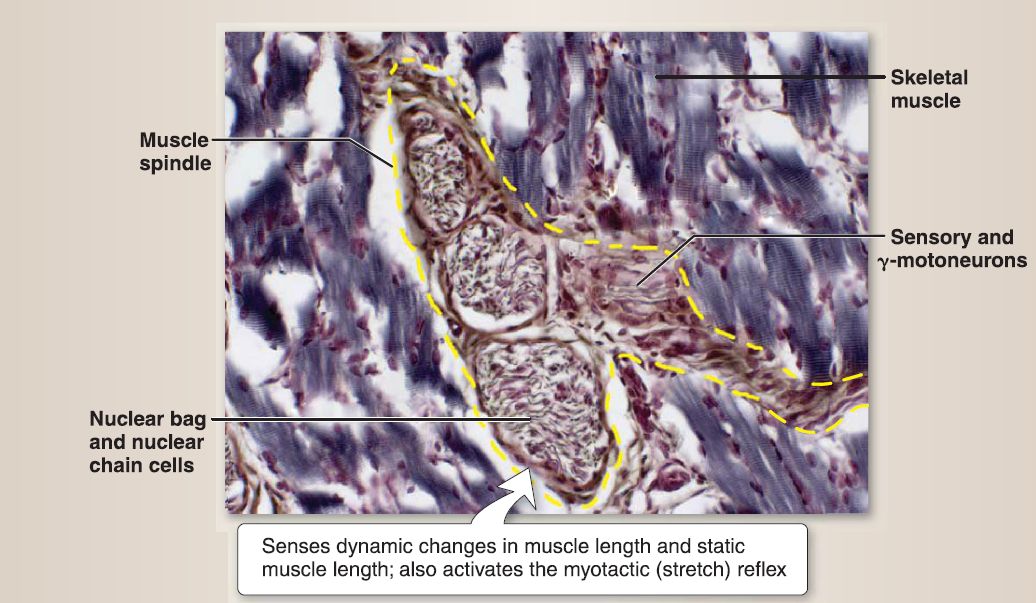 Figure 6: Muscle spindle (yellow dashed line).
Figure 6: Muscle spindle (yellow dashed line).



|
|
|
|
دراسة تحدد أفضل 4 وجبات صحية.. وأخطرها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تحتفي بذكرى ولادة الإمام محمد الجواد (عليه السلام)
|
|
|