


 النبات
النبات
 الحيوان
الحيوان
 الأحياء المجهرية
الأحياء المجهرية
 علم الأمراض
علم الأمراض
 التقانة الإحيائية
التقانة الإحيائية
 التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
التقنية الحيوية المكروبية
 التقنية الحياتية النانوية
التقنية الحياتية النانوية
 علم الأجنة
علم الأجنة
 الأحياء الجزيئي
الأحياء الجزيئي
 علم وظائف الأعضاء
علم وظائف الأعضاء
 الغدد
الغدد
 المضادات الحيوية
المضادات الحيوية|
Read More
Date: 29-8-2021
Date: 12-11-2021
Date: 10-9-2021
|
Fatty Acid Structure
A fatty acid consists of a hydrophobic hydrocarbon chain with a terminal carboxyl group that has a pKa (see p. 6) of ~4.8 (Fig. 1). At physiologic pH, the terminal carboxyl group (–COOH) ionizes, becoming –COO−. [Note: When the pH is above the pK, the deprotonated form predominates .] This anionic group has an affinity for water, giving the fatty acid its amphipathic nature (having both a hydrophilic and a hydrophobic region). However, for longchain-length fatty acids (LCFA), the hydrophobic portion is predominant. These molecules are highly water insoluble and must be transported in the circulation in association with protein. More than 90% of the fatty acids found in plasma are in the form of fatty acid esters (primarily TAG, cholesteryl esters, and phospholipids) contained in circulating lipoprotein particles . FFA are transported in the circulation in association with albumin, the most abundant protein in serum.
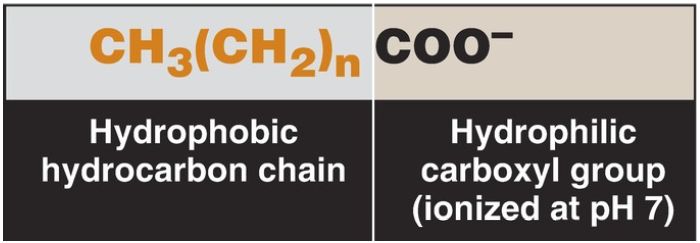
Figure 1: Structure of a fatty acid.



|
|
|
|
تحذير من "عادة" خلال تنظيف اللسان.. خطيرة على القلب
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
دراسة علمية تحذر من علاقات حب "اصطناعية" ؟!
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية المقدسة تؤكد أهمية المضي في طريق العفاف والاقتداء بأهل البيت (عليهم السلام)
|
|
|