


 Grammar
Grammar
 Tenses
Tenses
 Present
Present
 Past
Past
 Future
Future
 Parts Of Speech
Parts Of Speech
 Nouns
Nouns
 Verbs
Verbs
 Adverbs
Adverbs
 Adjectives
Adjectives
 Pronouns
Pronouns
 Pre Position
Pre Position
 Preposition by function
Preposition by function 
 Preposition by construction
Preposition by construction
 Conjunctions
Conjunctions
 Interjections
Interjections
 Grammar Rules
Grammar Rules
 Linguistics
Linguistics
 Semantics
Semantics
 Pragmatics
Pragmatics
 Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension|
Read More
Date: 2024-03-13
Date: 2023-11-24
Date: 2024-04-30
|
In the Korean case which we just considered, it happens that the underlying form of the word is the same as the way the word is pronounced when it is said alone. This situation does not hold in Matuumbi, where one has to know how a word is pronounced when it is not at the end of an utterance, in order to determine the underlying form of the word. The words in (25) have an H tone (marked with an acute accent) on the second vowel from the beginning of the word when said alone. When another word follows, they seem to lose that H tone.

In contrast, the words of (26), which also have an H tone on the second vowel from the beginning of the word when the word is said alone, keep their H tone when another word follows.

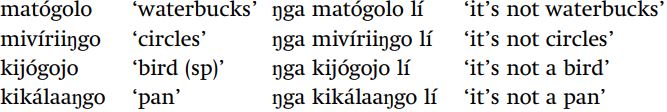
There are no words in Matuumbi which are toneless when said by themselves, thus *kitekeljo said by itself is an unattested kind of word. There is a clear contrast in tonal behavior between the words in (25), where the presence of an H tone on the second vowel depends on whether the word is said alone or is followed by another word, and those in (26), where the second vowel always has an H tone. The solution to this puzzle is that the words in (26) have an underlying H tone on their second vowel, and thus nothing happens to that tone; but the words in (25) have no underlying H, and instead get an H at the end of an utterance by a rule that assigns an H tone to the second vowel of a toneless word which comes at the end of an utterance. Thus in the case of Matuumbi tone, the contrast between underlyingly toneless words and words with underlying H is best revealed by looking at the word when it appears not by itself: it is the citation form of the word that undergoes the neutralization rule, which is the opposite of the situation we just encountered in Korean.
|
|
|
|
دراسة تحدد أفضل 4 وجبات صحية.. وأخطرها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
العتبة العباسية تستعدّ لتكريم عددٍ من الطالبات المرتديات للعباءة الزينبية في جامعات كركوك
|
|
|