

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Complement system
المؤلف:
Abbas, A. K., Lichtman, A. H., & Pillai, S
المصدر:
Basic Immunology : Function and disorders of immune system
الجزء والصفحة:
6th ed , page 39-40
2025-01-16
1155
The complement system is a collection of circulating and membrane-associated proteins that are important in defense against microbes. Many complement proteins are proteolytic enzymes, and complement activation involves the sequential activation of these enzymes. The complement cascade may be initiated by any of three pathways (Fig. 1):
• The alternative pathway is triggered when some complement proteins are activated on microbial surfaces and cannot be controlled, because complement regulatory proteins are not present on microbes (but are present on host cells). The alternative pathway is a component of innate immunity.
• The classical pathway is most often triggered by antibodies that bind to microbes or other antigens and is thus a component of the humoral arm of adaptive immunity.
• The lectin pathway is activated when a carbohydrate-binding plasma protein, mannose-binding lectin (MBL), binds to its carbohydrate ligands on microbes. This lectin activates proteins of the classical pathway, but because it is initiated by a microbial product in the absence of antibody, it is a component of innate immunity.
Activated complement proteins function as proteolytic enzymes to cleave other complement proteins. Such an enzymatic cascade can be rapidly amplified because each proteolytic step generates many products that are themselves enzymes in the cascade. The central component of all three complement pathways is a plasma protein called C3, which is cleaved by enzymes generated in the early steps. The major proteolytic fragment of C3, called C3b, becomes covalently attached to microbes and is able to recruit and activate downstream complement proteins on the microbial surface. The three path ways of complement activation differ in how they are initiated, but they share the late steps and perform the same effector functions. T he complement system serves three main functions in host defense:
• Opsonization and phagocytosis. C3b coats microbes and promotes the binding of these microbes to phagocytes by virtue of receptors for C3b that are expressed on the phagocytes. Thus, microbes that are coated with complement proteins are rapidly ingested and destroyed by phagocytes. This process of coating a microbe with molecules that are recognized by receptors on phagocytes is called opsonization.
• Inflammation. Some proteolytic fragments of complement proteins, especially C5a and C3a, are chemoattractants for leukocytes (mainly neutrophils and monocytes), and they also are activators of endothelial cells and mast cells. Thus, they promote movement of leukocytes and plasma proteins into tissues (inflammation) at the site of complement activation.
• Cell lysis. Complement activation culminates in the formation of a polymeric protein complex that inserts into the microbial cell membrane, disturbing the permeability barrier and causing osmotic lysis.
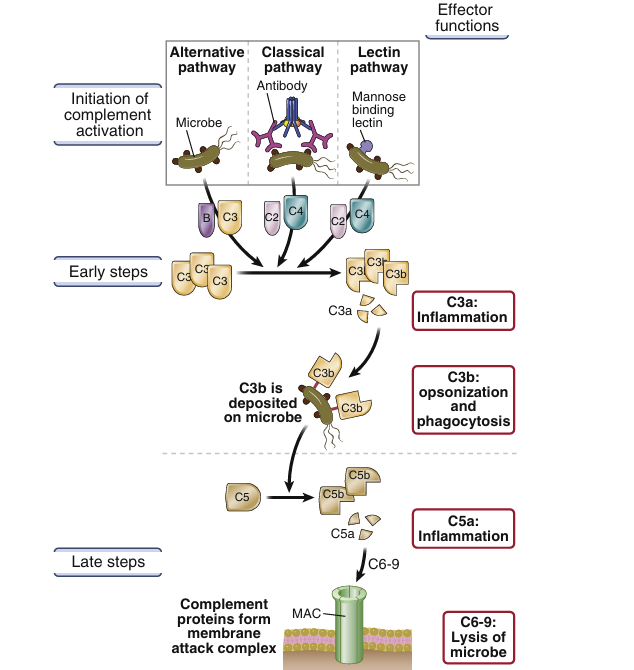
Fig. 1 Pathways of complement activation. The activation of the complement system (the early steps) may be initiated by three distinct pathways, all of which lead to the production of C3b. C3b initiates the late steps of complement activation, culminating in the formation of a multiprotein complex called the membrane attack complex (MAC), which is a transmembrane channel composed of polymerized C9 molecules that causes lysis of thin-walled microbes. Peptide by-products released during complement activation are the inflammation-inducing C3a and C5a.
 الاكثر قراءة في المناعة
الاكثر قراءة في المناعة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















