

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Fab, Fc, and Hinge Molecular Components
المؤلف:
Mary Louise Turgeon
المصدر:
Immunology & Serology in Laboratory Medicine
الجزء والصفحة:
5th E , P16-17
2025-01-27
834
A typical monomeric IgG molecule consists of three globular regions (two Fab regions and an Fc portion) linked by a flexible hinge region. If the molecule is digested with a proteolytic enzyme such as papain, it splits into three approximately equal sized fragments (Fig. 1). Two of these fragments retain the ability to bind antigen and are called the antigen-binding fragments (Fab fragments). The third fragment, which is relatively homogeneous and is sometimes crystallizable, is called the Fc portion. If IgG is treated with another proteolytic enzyme, pepsin, the molecule separates somewhat differently. The Fc fragment is split into tiny peptides and thus is completely destroyed. The two Fab fragments remain joined to produce a fragment called F(ab)′2. This fragment possesses two antigen binding sites. If F(ab)′2 is treated to reduce its disulfide bonds, it breaks into two Fab fragments, each of which has only one antigen-binding site. Further disruption of the interchain disulfide bonds in the Fab fragments shows that each contains a light chain and half of a heavy chain, which is called the Fd fragment.
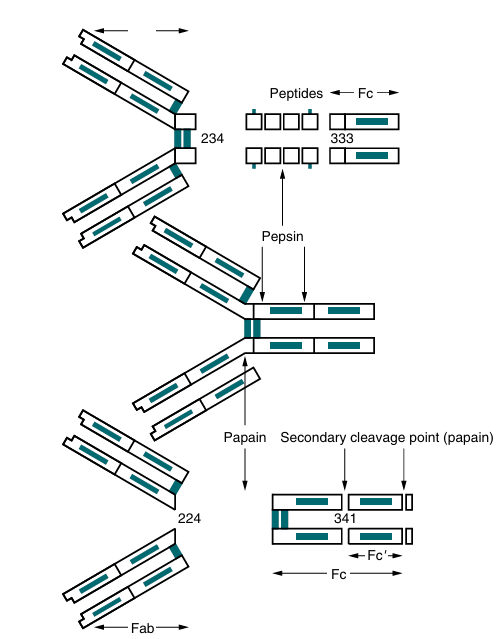
fig1. Enzymatic cleavage of human IgG1. (Adapted from Tur geon ML: Fundamentals of immunohematology, ed 2, 1995, Williams & Wilkins.)
Electron microscopy studies of IgG have revealed that the Fab regions of the molecule are mobile and can swing freely around the center of the molecule as if it were hinged. This hinge consists of a group of about 15 amino acids located between the CH1 and CH2 regions. The exact sequence of amino acids in the hinge is variable and unique for each Ig class and subclass. Because amino acids can rotate freely around peptide bonds, the effect of closely spaced proline amino acid residues is production of a so-called universal joint, around which the Ig chains can swing freely. A remarkable feature of the hinge region is the presence of a large number of hydrophilic and proline residues. The hydrophilic residues tend to open up this region and thus make it accessible to proteolytic cleavage with enzymes such as pepsin and papain. This region also contains all the interchain disulfide bonds except for IgD, which has no interchain links.
 الاكثر قراءة في المناعة
الاكثر قراءة في المناعة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















