

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Antigens Recognized by T Lymphocytes
المؤلف:
Abbas, A. K., Lichtman, A. H., & Pillai, S
المصدر:
Basic Immunology : Function and disorders of immune system
الجزء والصفحة:
6th ed , page 52
2025-02-12
1090
The majority of T lymphocytes recognize peptide anti gens that are bound to and displayed by the MHC molecules of antigen-presenting cells (APCs). The MHC is a genetic locus whose principal protein products function as the peptide display molecules of the immune system. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells can see peptides only when these peptides are displayed by that individual’s MHC molecules. This property of T cells is called MHC restriction. The T cell receptor (TCR) recognizes some amino acid residues of the peptide antigen and simultaneously also recognizes residues of the MHC molecule that is displaying that peptide (Fig. 1). Each TCR, and hence each clone of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells, recognizes one peptide displayed by one of the many MHC molecules in every individual. Also, some small populations of T cells recognize lipid and other nonpeptide antigens either presented by nonpolymorphic class I MHC–like molecules or without a requirement for a specialized antigen display system.
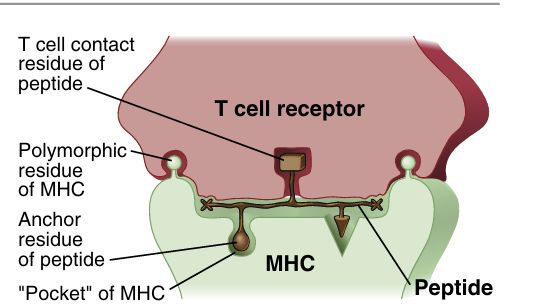
fig1. Model showing how a T cell receptor recognizes a complex of peptide antigen displayed by an MHC molecule. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules are expressed on antigen-presenting cells and function to display peptides derived from protein antigens. Peptides bind to the MHC molecules by anchor residues, which attach the peptides to pockets in the MHC molecules. The antigen receptor of every T cell recognizes some amino acid residues of the pep tide and some (polymorphic) residues of the MHC molecule.
The cells that capture microbial antigens and dis play them for recognition by T lymphocytes are called antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Naive T lymphocytes must see protein antigens presented by dendritic cells to initiate clonal expansion and differentiation of the T cells into effector and memory cells. Differentiated effector T cells again need to see antigens, which may be presented by various kinds of APCs besides dendritic cells, to activate the effector functions of the T cells in both humoral and cell-mediated immune responses. We first describe how APCs capture and present antigens to trigger immune responses and then examine the role of MHC molecules in antigen presentation to T cells.
 الاكثر قراءة في المناعة
الاكثر قراءة في المناعة
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















