

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Laboratory Diagnosis of Cancer
المؤلف:
Bezabeh ,M. ; Tesfaye,A.; Ergicho, B.; Erke, M.; Mengistu, S. ; Bedane,A. and Desta, A
المصدر:
General Pathology
الجزء والصفحة:
19-2-2016
1857
Laboratory Diagnosis of Cancer
Every year approach to laboratory diagnosis of cancer becomes more complex more sophisticated and more specialized with time.
Histologic and cytologic methods:
- The laboratory diagnoses of most cancers is not difficult however, border line cases in no man's land where wise men trade cautiously pose the most difficulties
- Clinicians tend to underestimate the important contributions they make in the diagnosis of neoplasms. Clinical data are invaluable for optimal pathologic diagnosis for example radiation changes in the skin or mucosa can be similar to cancer and similarly section taken from a healing fracure can mimic remarkably an osteosarcoma.
- The laboratory sample to be diagnosed need to be adequate, representative and well preserved
Several sampling approaches are available:
1. Excisional or incisional biopsy
2. Cytologic smears:
Fine needle aspiration
PAP smear
Fluid cytology
3. Advanced techniques
Immunocytochemistry
Flow cytometry
Tumour markers
Excisional biopsy
- Selection of an appropriate site for biopsy of a large mass requires awareness that the margins may not be representative and the center largely necrotic .analogously disseminated lymphoma involving inguinal lymph nodes that drain large part of the body often have reactive changes that may mask neoplastic involvement.
- Appropriate preservation of specimens is obvious thus, formalin for routine fixation glutaraldehyde for electron microscopy prompt refrigeration to permit optimal hormone by receptor analysis
- Requesting, “quick frozen section" diagnosis is sometimes desirable for determining (for example in breast carcinoma) for evaluating the margins of an excised cancer to ascertain that the entire neoplasm has been removed.
Fine needle aspiration
- The procedure involves aspirating cell and attendant fluid with a small needle followed by cytologic examination of the stained smear
- This method is used most commonly for the assessment of readily palpable lesions such as breasts, thyroid and lymph nodes etc.
Cytologic (PAP) smear
- This method is widely used for the discovery of carcinoma of the cervix, it also detect cervical cancers at an in situ stage, and other suspected malignancies such as endometrial, and bronchogenic carcinomas, bladder and prostatic tumours and gastric carcinoma.
- It is also used for the identification of tumour cell in abdominal, pleural joint and cerebrospinal fluids
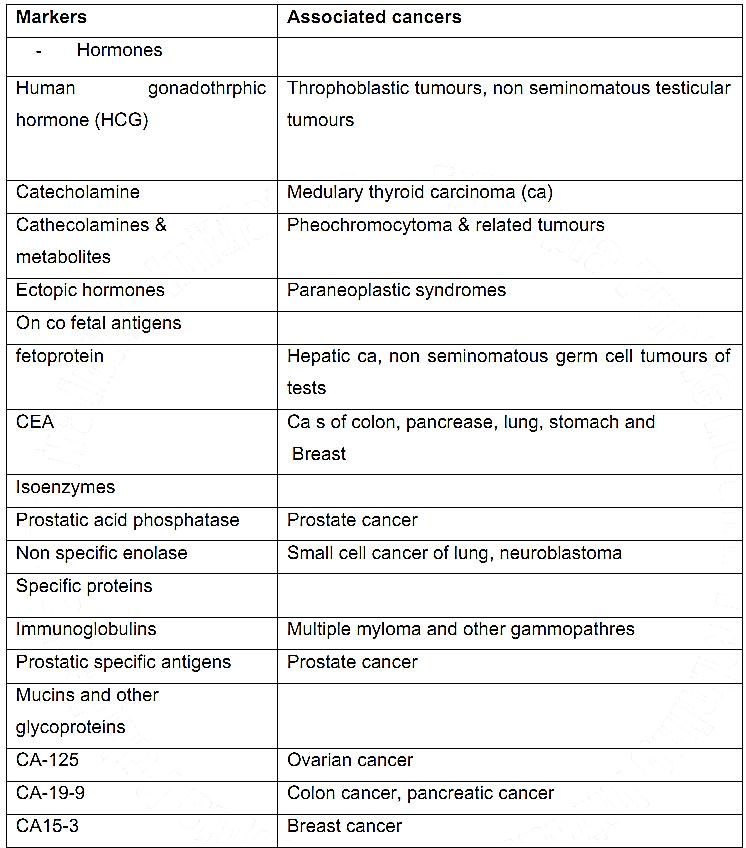
Tumour markers
- Tumour markers are biochemical indicators of the presence of a tumour. They include cell surface antigens, cytoplasmic proteins, enzymes and hormones.
- Tumour markers cannot be construed as primary modalities for the diagnosis of cancer and thus, act as supportive laboratory tests.
- A host of tumour markers have been described and new only appear every year
Selected Tumor Markers
New advanced techniques are being constantly added to the tools of the surgical pathologists, which include:
1. Immunocytochemistry
The availability of specific monoclonal antibodies has greatly facilitates the identification of cell products and surface markers. Some examples of utility of immunocyto chemistry in the diagnosis of malignant neoplasms are
- Categorization of undifferentiated malignant tumours here intermediate filaments are important. Keratin for carcinomas, desmin for neoplasm’s of muscle origin
- Categorization of leukemias / lymphomas
- Determination of site of origin of metastatic tumours
- Detection of molecules that have prognostic or therapeutic significance: Detection of hormone ( estrogen /progesterone) receptors in breast cancer cells is of prognostic and therapeutic value because these cancers are susceptible to anti-estrogen therapy .Protein products of oncogen such as C- erb B2 in breast cancer are prognosis
- Prognosis of malignant neoplasms
- Detection of minimal residual disease
- Diagnosis of hereditary predisposition cancer
2 . Flow Cytometry
- identification of cell surface antigens by flow Cytometry is widely used in the classification of leukemias and lymphomas Follow Cytometry is used for detection of aneuploidy which is also associated with poorer prognosis in early stage breast cancer carcinomas of the urinary bladder lung cancer colorectal cancer, and prostate cancer
References
Bezabeh ,M. ; Tesfaye,A.; Ergicho, B.; Erke, M.; Mengistu, S. and Bedane,A.; Desta, A.(2004). General Pathology. Jimma University, Gondar University Haramaya University, Dedub University.
 الاكثر قراءة في الاورام
الاكثر قراءة في الاورام
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















