
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Our Sun
المؤلف:
Diane Fisher Miller
المصدر:
Basics of Radio Astronomy
الجزء والصفحة:
p54
2-3-2016
2275
Our Sun
The strongest extraterrestrial radio source we experience here on Earth is our own star. The Sun is a very ordinary star not particularly massive or small, not particularly hot or cold, not particularly young or old. Perhaps we are fortunate it is so typical because from it we can learn much about stars in general.
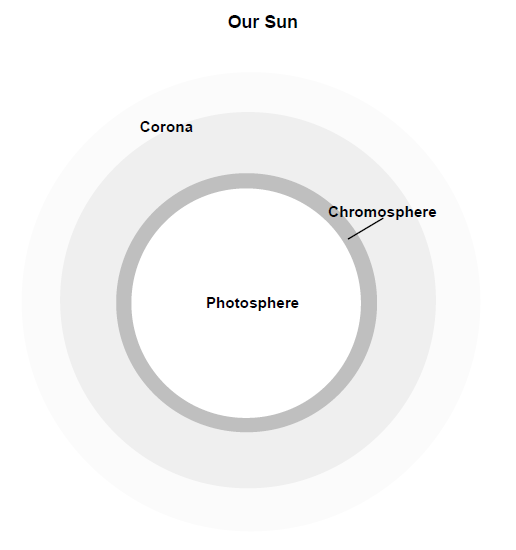
The photosphere is the part of the sun’s atmosphere that emits most of the visible light, while the corona, the sun’s outer atmosphere, is much less dense and emits only a very small amount of visible light. The chromosphere, cool and dim compared to the photosphere, forms the boundary between the photosphere and the corona.
The sun seems to have about an 11-year cycle of activity. When the sun is in a quiet phase, radio emissions from the photosphere (the part that also emits radiation in the visible wavelength) are in the wavelength range of 1 cm, while radio emissions from the corona approach a wavelength of one meter. The size of the radio solar disk appears only slightly larger than the optical solar disk as long as the telescope is tuned to only the 1-cm to 10-cm wavelength range. But at the longer wavelengths, the radio solar disk is much larger, including, as it does, the corona, which extends millions of kilometers above the photosphere.
Sunspots are darker appearing areas on the photosphere, and, as mentioned above, they seem to fluctuate in frequency over about an 11-year cycle. They appear darker because they are a “cool” 4,000°C relative to the surrounding 6,000°C surface. They are the centers of magnetic fields, apparently related to the sun’s magnetic field. It is possible that the sun’s magnetic lines of force periodically get “tangled” and destabilized since the sun’s rate of rotation varies from the equator to the poles. Solar flares breaking out of the sun’s upper atmosphere are usually associated with sunspot groups.
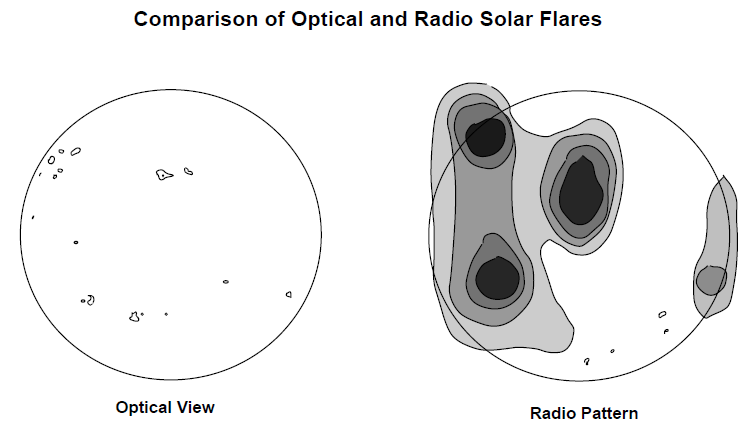
Solar flares emit short bursts of radio energy, with wavelengths observable from the ground from about 1 to 60 m (300-5 MHz). Sometimes during intense flares, a stream of high-energy cosmic ray particles is emitted, travelling at over 500-1000 km per sec. When these charged particles reach Earth’s magnetic field, we get magnetic storms and the aurora. The pattern of radio emissions from solar flares appears to originate from a larger area of the solar surface than does the pattern of visible-range radiation, but it is still apparent that they are the result of the same activity.
The radiation associated with solar flares is circularly polarized, rather than randomly polarized as is usual from extraterrestrial sources. This polarization may be caused by electrons gyrating in the localized, intense magnetic field of the flare.
The sun is studied by radio astronomers both directly, by observing the actual radio emissions from the sun, and indirectly, by observing the effect of the sun’s radiation on Earth’s ionosphere.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















