
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
EMISSION OF THERMAL LIGHT
المؤلف:
Mark Csele
المصدر:
FUNDAMENTALS OF LIGHT SOURCES AND LASERS
الجزء والصفحة:
p1
8-3-2016
3004
EMISSION OF THERMAL LIGHT
We have all undoubtedly encountered thermal light in the form of emission of light from a red-hot object such as an element on an electric stove. Other examples of such light are in the common incandescent electric lamp, in which electrical current flowing through a thin filament of tungsten metal heats it until it glows white-hot. The energy is supplied by an electrical current in what is called resistance heating, but it could just as well have been supplied by, say, a gas flame. In fact, the original incandescent lamp was developed in 1825 for use in surveying Ireland and was later used in lighthouses. The lamp worked by spraying a mixture of oxygen and alcohol (which burns incredibly hot) at a small piece of lime and igniting it. The lime was placed at the hottest part of the flame and heated until it glowed white-hot, emitting an immense quantity of light. It was the brightest form of artificial illumination at the time and was claimed to be 83 times as bright as conventional gas lights of the time. Improvements to the lamp were made by using a parabolic reflector behind the piece of lime concentrating the light. The lamp allowed the surveying of two mountain peaks over 66 miles apart and was later improved by using hydrogen and oxygen as fuel but eventually was superseded by the more convenient electric arc lamp. This light source did, however, find its way into theaters, where it was used as a
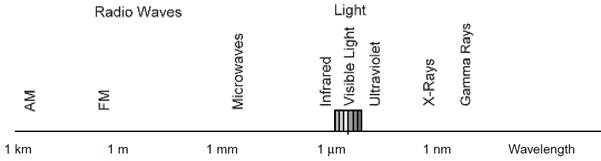
Figure 1.1 Electromagnetic spectrum.
spotlight which replaced the particularly dangerous open gas flames used at the time for illumination, and hence the term limelight was born.
 الاكثر قراءة في الضوء
الاكثر قراءة في الضوء
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















