


 علم الكيمياء
علم الكيمياء 
 الكيمياء التحليلية
الكيمياء التحليلية 
 الكيمياء الحياتية
الكيمياء الحياتية 
 الكيمياء العضوية
الكيمياء العضوية 
 الكيمياء الفيزيائية
الكيمياء الفيزيائية
 الكيمياء اللاعضوية
الكيمياء اللاعضوية 
 مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
مواضيع اخرى في الكيمياء
 الكيمياء الصناعية
الكيمياء الصناعية |
Read More
Date: 5-9-2017
Date: 10-9-2017
Date: 6-9-2017
|
EXTRACTION OFAROMATICS
Benzene, toluene, xylenes (BTX), and ethylbenzene are obtained mainly from the catalytic reforming of heavy naphtha. The product reformate is rich in C6, C7, and C8 aromatics, which could be extracted by a suitable solvent such as sulfolane or ethylene glycol. These solvents are characterized by a high affinity for aromatics, good thermal stability, and rapid phase separation. The Tetra extraction process by Union Carbide (Figure 1) uses tetraethylene glycol as a solvent. The feed (reformate), which contains a mixture of aromatics, paraffins, and naphthenes, after heat exchange with hot raffinate, is countercurrentIy contacted with an aqueous tetraethylene lycol solution in the extraction column.
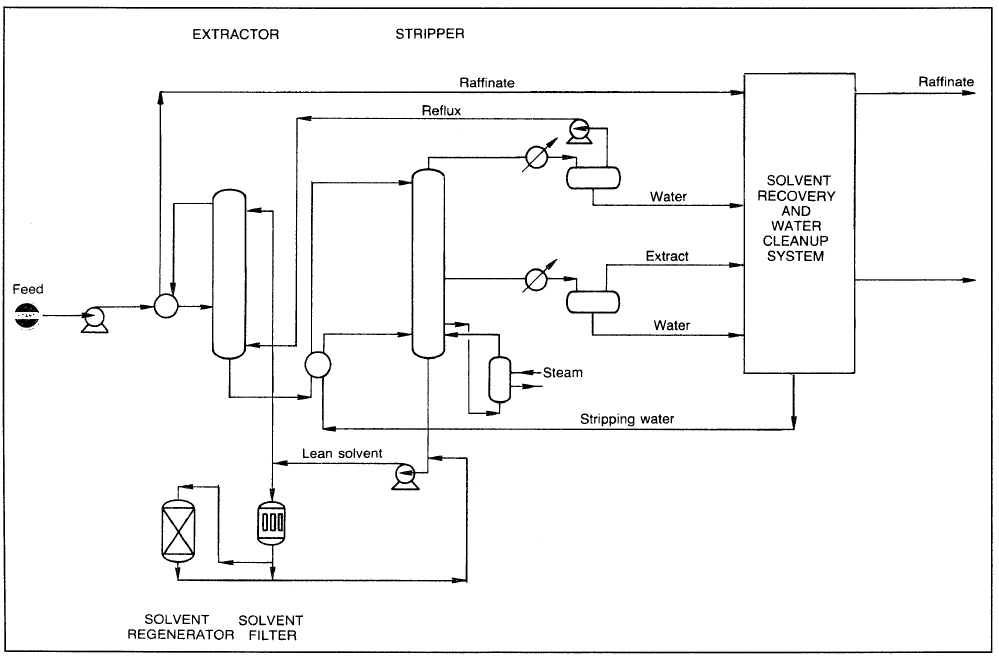
Figure 1. The Union Carbide aromatics extraction process using tetraethylene glycol.
The hot, rich solvent containing BTX aromatics is cooled and introduced into the top of a stripper column. The aromatics extract is then purified by extractive distillation and recovered from the solvent by steam stripping. Extractive distillation has been reviewed by Gentry and Kumar. The raffinate (constituted mainly of paraffins, isoparaffins and cycloparaffins) is washed with water to recover traces of solvent and then sent to storage. The solvent is recycled to the extraction tower. The extract, which is composed of BTX and ethylbenzene, is then fractionated. Benzene and toluene are recovered separately, and ethylbenzene and xylenes are obtained as a mixture (C8 aromatics).
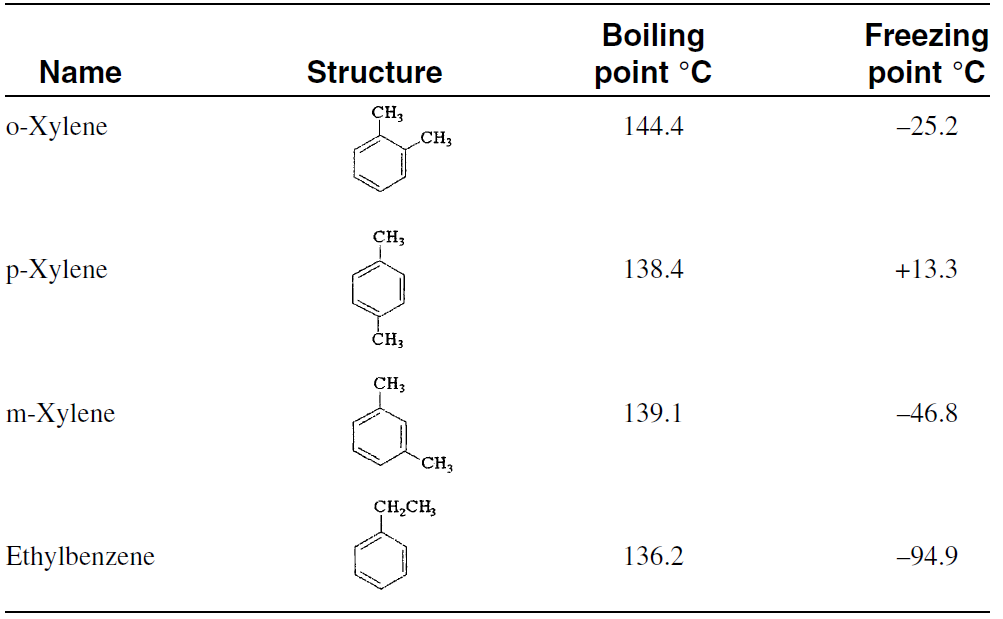
Due to the narrow range of the boiling points of C8 aromatics (Table 1-1), separation by fractional distillation is difficult. A superfractionation technique is used to segregate ethylbenzene from the xylene mixture. Because p-xylene is the most valuable isomer for producing synthetic fibers, it is usually recovered from the xylene mixture. Fractional crystallization used to be the method for separating the isomers, but the yield was only 60%. Currently, industry uses continuous liquid-phase adsorption separation processes.
Table 1-1 : Boiling and freezing points of C8 aromatics
The overall yield of p-xylene is increased by incorporating an isomerization unit to isomerize o- and m-xylenes to p-xylene. An overall yield of 90% p-xylene could be achieved. Figure 2 is a flow diagram of the Mobil isomerization process. In this process, partial conversion of ethylbenzene to benzene also occurs. The catalyst used is shape selective and contains ZSM-5 zeolite.

Figure 2. Flow diagram of the Mobil xylene isomerization process.



|
|
|
|
لصحة القلب والأمعاء.. 8 أطعمة لا غنى عنها
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
حل سحري لخلايا البيروفسكايت الشمسية.. يرفع كفاءتها إلى 26%
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
جامعة الكفيل تحتفي بذكرى ولادة الإمام محمد الجواد (عليه السلام)
|
|
|