

النبات

مواضيع عامة في علم النبات

الجذور - السيقان - الأوراق

النباتات الوعائية واللاوعائية

البذور (مغطاة البذور - عاريات البذور)

الطحالب

النباتات الطبية


الحيوان

مواضيع عامة في علم الحيوان

علم التشريح

التنوع الإحيائي

البايلوجيا الخلوية


الأحياء المجهرية

البكتيريا

الفطريات

الطفيليات

الفايروسات


علم الأمراض

الاورام

الامراض الوراثية

الامراض المناعية

الامراض المدارية

اضطرابات الدورة الدموية

مواضيع عامة في علم الامراض

الحشرات


التقانة الإحيائية

مواضيع عامة في التقانة الإحيائية


التقنية الحيوية المكروبية

التقنية الحيوية والميكروبات

الفعاليات الحيوية

وراثة الاحياء المجهرية

تصنيف الاحياء المجهرية

الاحياء المجهرية في الطبيعة

أيض الاجهاد

التقنية الحيوية والبيئة

التقنية الحيوية والطب

التقنية الحيوية والزراعة

التقنية الحيوية والصناعة

التقنية الحيوية والطاقة

البحار والطحالب الصغيرة

عزل البروتين

هندسة الجينات


التقنية الحياتية النانوية

مفاهيم التقنية الحيوية النانوية

التراكيب النانوية والمجاهر المستخدمة في رؤيتها

تصنيع وتخليق المواد النانوية

تطبيقات التقنية النانوية والحيوية النانوية

الرقائق والمتحسسات الحيوية

المصفوفات المجهرية وحاسوب الدنا

اللقاحات

البيئة والتلوث


علم الأجنة

اعضاء التكاثر وتشكل الاعراس

الاخصاب

التشطر

العصيبة وتشكل الجسيدات

تشكل اللواحق الجنينية

تكون المعيدة وظهور الطبقات الجنينية

مقدمة لعلم الاجنة


الأحياء الجزيئي

مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي


علم وظائف الأعضاء


الغدد

مواضيع عامة في الغدد

الغدد الصم و هرموناتها

الجسم تحت السريري

الغدة النخامية

الغدة الكظرية

الغدة التناسلية

الغدة الدرقية والجار الدرقية

الغدة البنكرياسية

الغدة الصنوبرية

مواضيع عامة في علم وظائف الاعضاء

الخلية الحيوانية

الجهاز العصبي

أعضاء الحس

الجهاز العضلي

السوائل الجسمية

الجهاز الدوري والليمف

الجهاز التنفسي

الجهاز الهضمي

الجهاز البولي


المضادات الميكروبية

مواضيع عامة في المضادات الميكروبية

مضادات البكتيريا

مضادات الفطريات

مضادات الطفيليات

مضادات الفايروسات

علم الخلية

الوراثة

الأحياء العامة

المناعة

التحليلات المرضية

الكيمياء الحيوية

مواضيع متنوعة أخرى

الانزيمات
Ethyl-Nitrosourea
المؤلف:
اعداد المرجع الالكتروني للمعلوماتية
المصدر:
almerja.com
الجزء والصفحة:
5-5-2016
2924
Ethyl-Nitrosourea
1-Ethyl-1-nitrososurea (ENU) is an ethylating and carbamoylating agent that is used as a potent mutagen in the mouse. ENU is widely used in mutagenesis of male (stem cell spermatogonia; differentiating spermatogonia; post-spermatogonial stages) and female (oocytes) mouse germ cells, where it introduces intragenic mutations. However, it has also been used for mutagenesis in sperm and embryonic and primordial germ cells, as well as zygotes. Because of its germ cell potency, ENU is the most suitable chemical mutagen for the generation of desired new mutations in the mouse. A variety of ENU-induced mouse mutants have been used as animal models for human genetic diseases. To close the phenotype gap in the mouse, several ENU mutagenesis programs have been initiated. The phenotype gap describes the fact that, although a great number of mouse mutants exist, there is still little known about the specific phenotypes of these mice.
ENU is a yellow-pink crystalline substance, with a melting point of 103° to 104°C and a molecular mass of 117.10. The structural formula is shown in Figure 1. ENU is not stable under physiological conditions, having a half-life of 34.1 min at pH 7.0 and 37°C. Because ENU is sensitive to humidity and light, it is stored below –10°C.
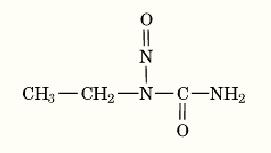
Figure 1. Structural formula of 1-ethyl-1-nitrosourea (ENU).
ENU produces mainly GC/AT transition mutations and, to a smaller extent, AT/GC, AT/CG, AT/TA, GC/CG, and GC/TA base substitutions. These effects are induced by ethylation of different positions within the four bases adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine, plus the phosphate groups of the DNA backbone. Additionally, ENU alkylates transfer RNA by the formation of 1,7-diethylguanosine. On removal of the ethyl group from O6-ethylguanine by the O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase (AGT), S-ethylcysteine is formed. ENU also reacts with chromosomal proteins (histones) to an even greater extent than other mutagens, eg, 1-methyl-1-nitrosourea or 1-n-propyl-nitrosourea. Proteins are carbamoylated by the degradation product of ENU, isocyanic acid. It is likely that carbamoylation of the nuclear proteins influences DNA–histone interactions.
In mouse mutagenesis studies, ENU is the preferred mutagen in spermatogonia, with a linear relationship between the induction of mutations and doses greater than 100 mg ENU/kg. At concentrations lower than 100 mg/kg, mutation induction is nonlinear, as a result of DNA repair processes in stem cell spermatogonia. The major mutagenic lesion is the formation of O6-ethylguanine. However, analysis of mouse hemoglobin mutants Hbb and Hba induced by ENU has shown that base substitutions at A and T can also occur. This contrasts with findings in other systems and emphasizes the complexity of in vivo mammalian germ cell mutagenesis. ENU is considered to be a supermutagen in mouse stem cell spermatogonia, inducing recessive mutations with a very high frequency. This mutation rate is maximized by repeated intraperitoneal injections of at least 100-mg ENU/kg at weekly intervals to a total dose of 300- to 400-mg ENU/kg.
Chemical mutagens have also been used to induce mutations in arrested and maturing oocytes of female mice. However, the mutation rate is significantly lower than for treated male germ cells. In addition, a high proportion of mutants derived from treatment of oocytes are mosaics, resulting from lesions affecting only one strand of the DNA. Treatment of oocytes also generates approximately 30% of large (multilocus) lesions. Only treatment of post-spermatogonial stages results in a higher percentage (65%) of such large lesions. The differences in the mutagenic potential of ENU on oocytes and stem cell spermatogonia occur mainly because oocytes are nondividing cells until fertilization. Consequently, mutagenesis of zygotes by an exposure of 50-mg ENU/kg at the time when the female genome enters metaphase II results in much higher mutation rates than in stem cell spermatogonia.
Different approaches have to be taken to recover a mutant mouse genotype. Dominant mutations can be screened directly in offspring of mutagenized males, whereas recessive mutations can be analyzed using a three-generation breeding protocol. Gene mutations in mouse germ or somatic cells by mutagens have been detected by the specific locus test, dominant cataract method, mouse spot test, micronucleus test, or new test systems like the MutaMouse or Big Blue mouse.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع عامة في الاحياء الجزيئي
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















