
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
Charge in Electric Field and Flashing Satellites
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn And Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 1 , p 37
13-7-2016
1665
Charge in Electric Field and Flashing Satellites
a) Write the relativistic equations of motion for a particle of charge and mass m in an electromagnetic field. Consider these equations for the special case of motion in the x direction only, in a Lorentz frame that has a constant electric field E pointing in the positive x direction.
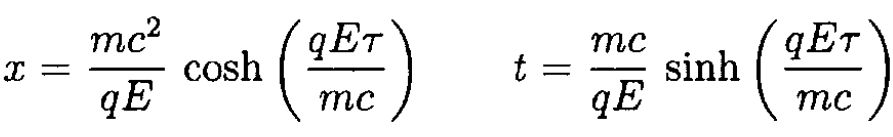 (i)
(i)
b) Show that a particular solution of the equations of motion is given by and show explicitly that the parameter τ used to describe the worldline of the charge q in equation (1) is the proper time along this worldline.
c) Define the acceleration 4-vector for this motion and show that it has constant magnitude. Draw a space-time (x, ct) diagram showing the worldline (1) and the direction of the acceleration vector at three typical points on the worldline (with τ < 0, τ = 0, τ > 0)
d) Suppose an observer moves along the worldline (1), starting at t = 0 and x = mc2/qE. Also, at τ = 0 she leaves behind a satellite that remains at rest at x = mc2/qE. The satellite emits flashes of light at a rate f that is constant in the satellite’s rest frame. Show that only a finite number mfc/qE of flashes ever reach the observer.
e) Some-time after τ = 0 the observer, always moving along the worldline (1), decides to retrieve the satellite. Show that she cannot wait longer than t = 3mc/4qE or τ = (mc/qE) sinh-1(3/4) to decide to do so.
Hint: To retrieve it at this limiting time, she must “reach down” to the satellite with the speed of light, bring it back at the speed of light, and wait indefinitely long for its return.
SOLUTION
Starting from a 4-vector potential(ϕ, A), we can obtain equations of motion for a charged particle in the electromagnetic field
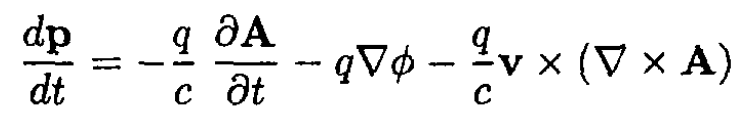 (1)
(1)
By definition
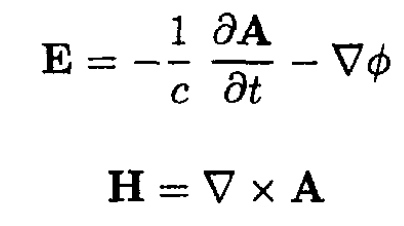
Therefore (1) becomes
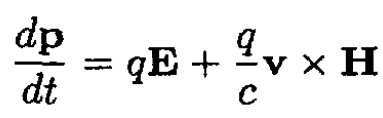 (2)
(2)
In this case of one-dimensional motion, where there is only an electric field E and momentum p in the x direction, we obtain
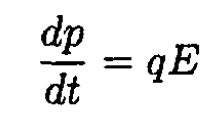 (3)
(3)
where
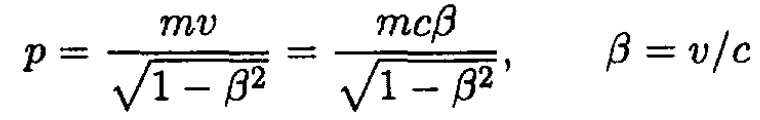 (4)
(4)
b) To show that (i) is a solution to (3), we write
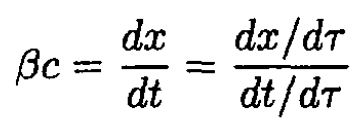
Now
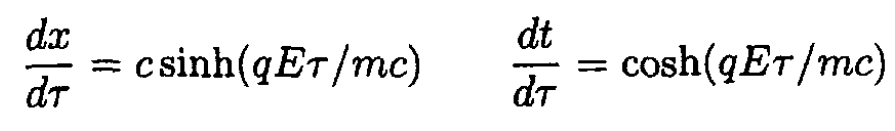
so
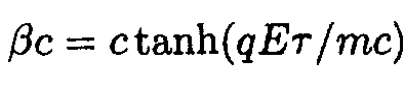
Since 1- tanh2 = 1/cosh2, we may rewrite (4)
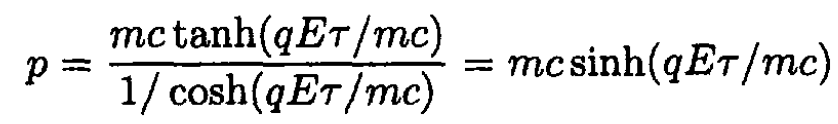
Differentiating,
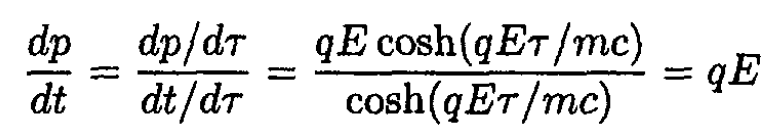
verifying (3). To show that τ is the proper time for the particle, we must demonstrate that
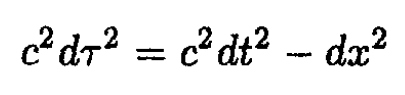
From (i)
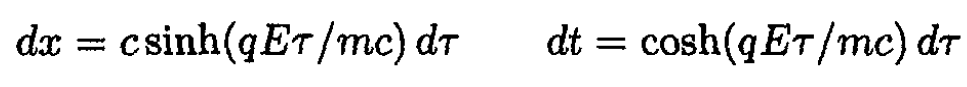
So
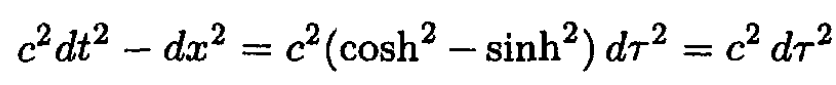
as required.
c) Define the 4-momentum as (ε/c, p, 0, 0), where ε is the energy ε = mc2γ and p is the momentum p = mc βγ. The 4-acceleration is given by (1/m)(dpμ /dτ)
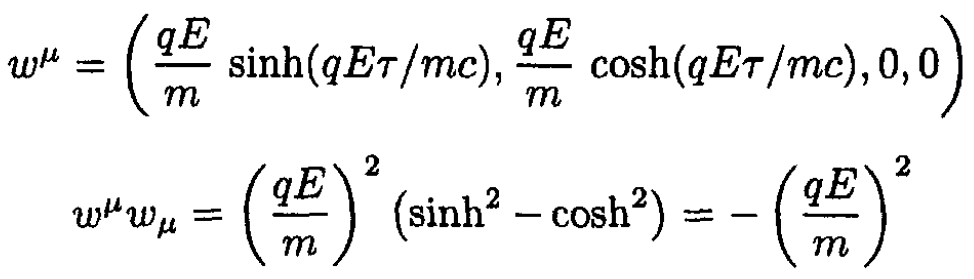
From (i), x2 – c2t2 = (mc2/qE)2, which defines a hyperbola (see Figure 1.1a).
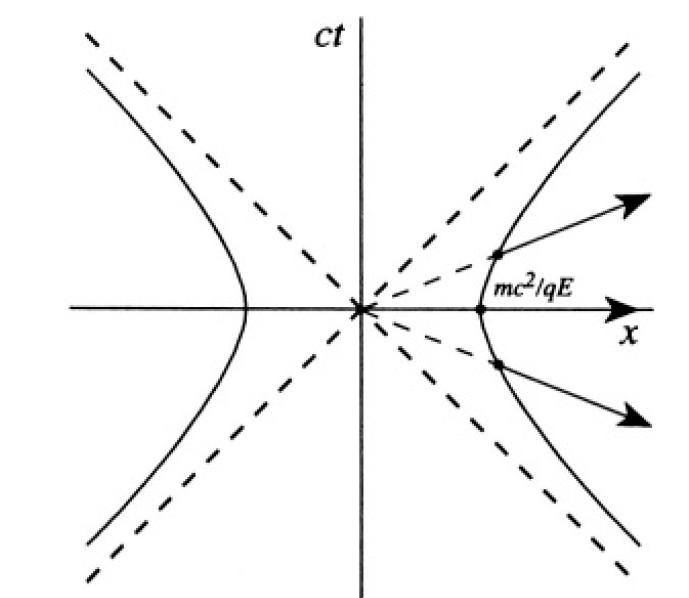
Figure 1.1a
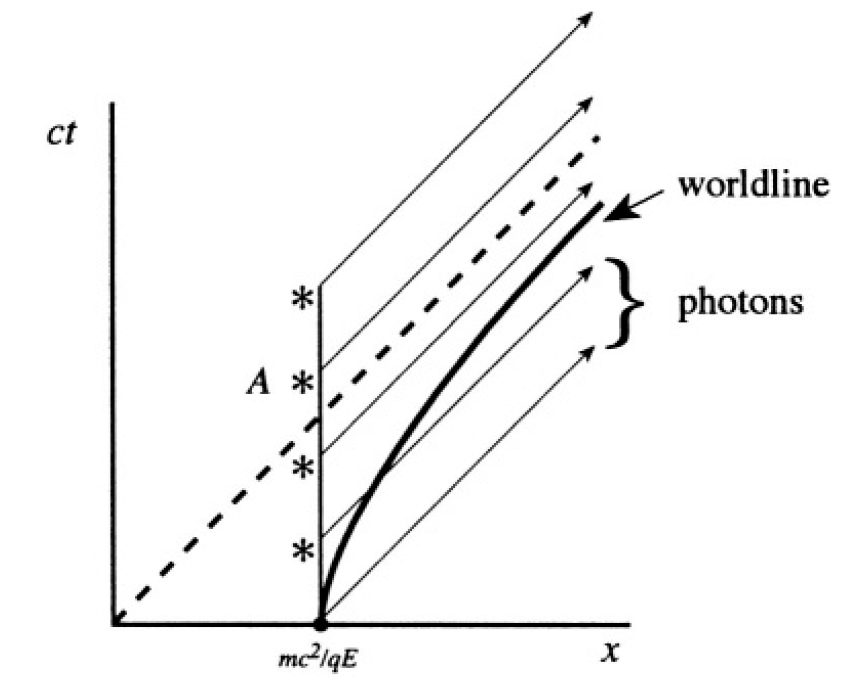
Figure 1.1b
d) From Figure 1.1b, we see that flashes emitted at a constant frequency f will cross the worldline of the particle until point A, where the trajectory of the satellite is above ct = x. To find the number of flashes, we find the time of intersection of x = mc2/qE and x = ct, i.e., t = mc/qE. The number of flashes is therefore ft = mcf/qE.
e) As shown in Figure 1.1c, we need the intersection of
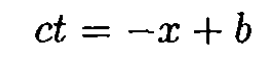
and
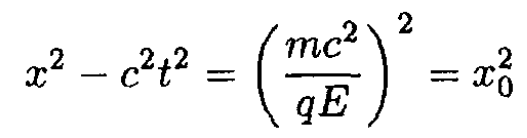
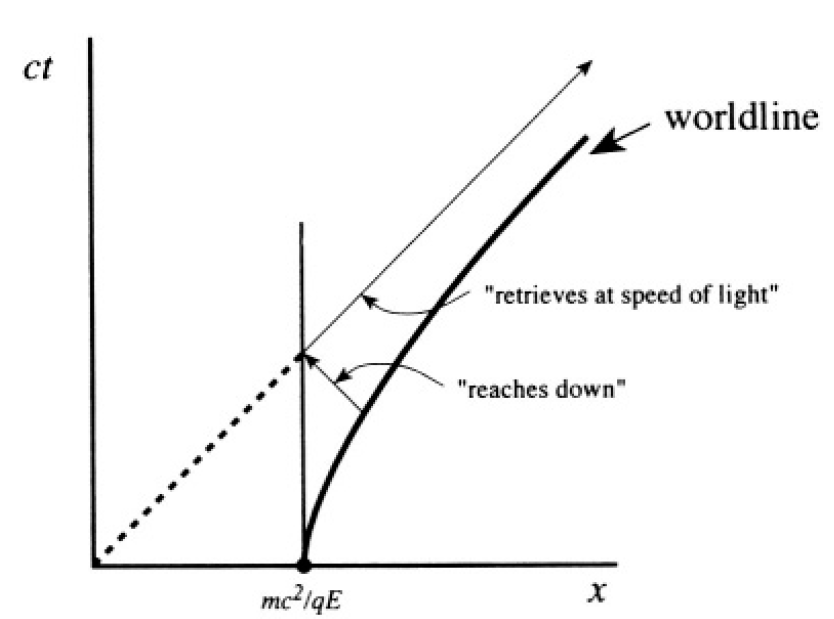
Figure 1.1c
where is found from
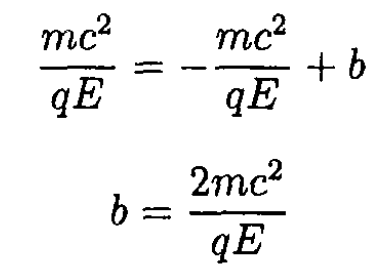
Thus,
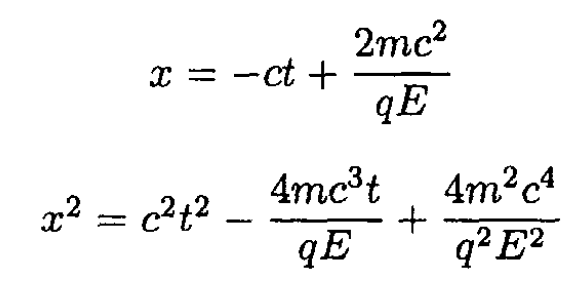
Therefore,
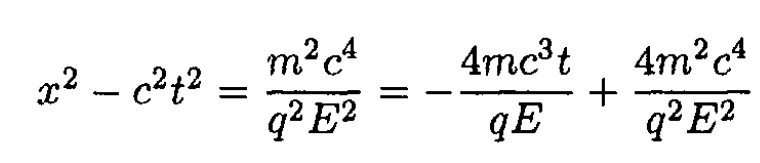
and
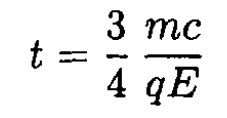 .
.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















