
تاريخ الفيزياء

علماء الفيزياء


الفيزياء الكلاسيكية

الميكانيك

الديناميكا الحرارية


الكهربائية والمغناطيسية

الكهربائية

المغناطيسية

الكهرومغناطيسية


علم البصريات

تاريخ علم البصريات

الضوء

مواضيع عامة في علم البصريات

الصوت


الفيزياء الحديثة


النظرية النسبية

النظرية النسبية الخاصة

النظرية النسبية العامة

مواضيع عامة في النظرية النسبية

ميكانيكا الكم

الفيزياء الذرية

الفيزياء الجزيئية


الفيزياء النووية

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء النووية

النشاط الاشعاعي


فيزياء الحالة الصلبة

الموصلات

أشباه الموصلات

العوازل

مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء الصلبة

فيزياء الجوامد


الليزر

أنواع الليزر

بعض تطبيقات الليزر

مواضيع عامة في الليزر


علم الفلك

تاريخ وعلماء علم الفلك

الثقوب السوداء


المجموعة الشمسية

الشمس

كوكب عطارد

كوكب الزهرة

كوكب الأرض

كوكب المريخ

كوكب المشتري

كوكب زحل

كوكب أورانوس

كوكب نبتون

كوكب بلوتو

القمر

كواكب ومواضيع اخرى

مواضيع عامة في علم الفلك

النجوم

البلازما

الألكترونيات

خواص المادة


الطاقة البديلة

الطاقة الشمسية

مواضيع عامة في الطاقة البديلة

المد والجزر

فيزياء الجسيمات


الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى

الفيزياء الكيميائية

الفيزياء الرياضية

الفيزياء الحيوية

الفيزياء والفلسفة

الفيزياء العامة


مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء

تجارب فيزيائية

مصطلحات وتعاريف فيزيائية

وحدات القياس الفيزيائية

طرائف الفيزياء

مواضيع اخرى
X-Ray Mirror
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn Boris E. Nadgorny
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
الجزء والصفحة:
part 1 , p 66
11-8-2016
2088
X-Ray Mirror
X-rays which strike a metal surface at an angle of incidence to the normal greater than a critical angle θ0 are totally reflected. Assuming that a metal contains n free electrons per unit volume, calculate θ0 as a function of the frequency ω of the X-rays. The metal occupies the region x > 0. The X-rays are propagating in the x-y plane (the plane of the picture) and their polarization vector is in the z direction, coming out of the picture (see Figure 1.1).

Figure 1.1
SOLUTION
Calculate the dielectric constant of the metal under the assumption that the electrons in metals are free and disregarding any scattering on the atoms, since they are much heavier than electrons (M >> m). Under the influence of the X-rays, the electrons only move a small fraction of the distance between atoms, so the field due to the atoms is nearly uniform over one period of the X-ray. Thus, we may write

Where E = E0ei(k.r – ωt), or
 (1)
(1)
The current density in the field is
 (2)
(2)
where n is the density of electrons in the metal. Using the Maxwell equation,
 (3)
(3)
Substituting (2) into (3), we have
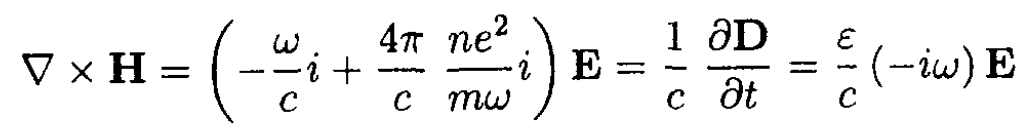 (4)
(4)
in which we used D = εE. From (4)
 (5)
(5)

Figure 1.2
For two media with ε2 < ε1 (see Figure 1.2),

For θ2 = π/2, the largest angle of refraction corresponds to the critical angle θ0 for the incident wave:

So

 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة

الآخبار الصحية















 قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة
قسم الشؤون الفكرية يصدر كتاباً يوثق تاريخ السدانة في العتبة العباسية المقدسة "المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة
"المهمة".. إصدار قصصي يوثّق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة فتوى الدفاع المقدسة للقصة القصيرة (نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)
(نوافذ).. إصدار أدبي يوثق القصص الفائزة في مسابقة الإمام العسكري (عليه السلام)


















