
β-decay of Tritium
 المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
 المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
 الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 70
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 70
 23-8-2016
23-8-2016
 1601
1601
β-decay of Tritium
Tritium is an isotope of hydrogen with one proton and two neutrons. A hydrogen-like atom is formed with an electron bound to the tritium nucleus. The tritium nucleus undergoes β-decay, and the nucleus changes its charge state suddenly to +2 and becomes an isotope of helium. If the electron is initially in the ground state in the tritium atom, what is the probability that the electron remains in the ground state after the sudden –β-decay?
SOLUTION
We use the sudden approximation to calculate the probability that the electron remains in the ground state. One calculates the overlap integral I of the initial and final wave functions, and its square is the probability. The ground states in the initial and final states are called ѱi and ѱf, and a0 is the Bohr radius:
 (1)
(1)
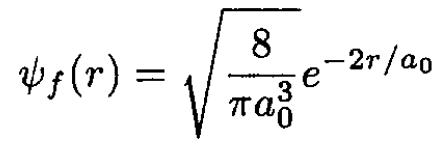 (2)
(2)
 (3)
(3)
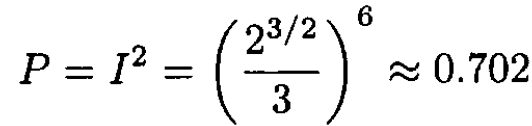 (4)
(4)
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


