
Gas Adsorption
 المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
 المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
 الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 47
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 47
 29-8-2016
29-8-2016
 1534
1534
Gas Adsorption
Consider a vapor (dilute monatomic gas) in equilibrium with a submonolayer (i.e., less than one atomic layer) of atoms adsorbed on a surface. Model the binding of atoms to the surface by a potential energy V = -ε0. Assume there are N0 possible sites for adsorption, and find the vapor pressure as a function of surface concentration θ = N/N0 (N is the number of adsorbed particles).
SOLUTION
For two systems in equilibrium, the chemical potentials should be equal. Consider one of the systems as an ideal gas (vapor) in a volume, and another as a surface submonolayer film. For an ideal gas the free energy F is given by
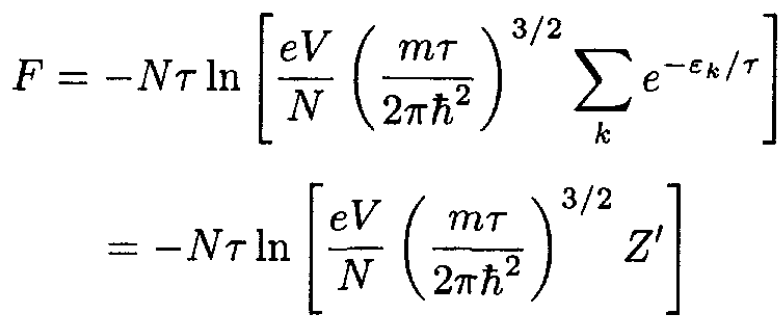 (1)
(1)
where εk and Z' correspond to the energy states and statistical sum associated with the internal degrees of freedom. If the temperature is reasonably small, τ << τion, where τion corresponds to the ionization energy of the atoms, so that the atoms are not ionized and mostly in the ground state, and this state is nondegenerate, we can take Z' = 1, and then (1) becomes
 (2)
(2)
The Gibbs free energy G is given by
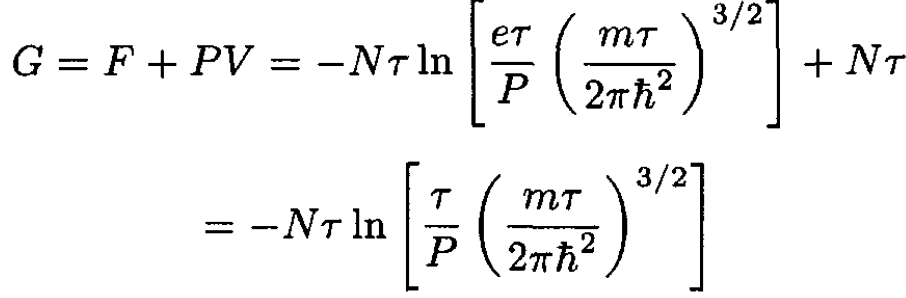 (3)
(3)
where we have expressed G as a function of P and τ, using PV = Nτ. The chemical potential μ = G/N, so
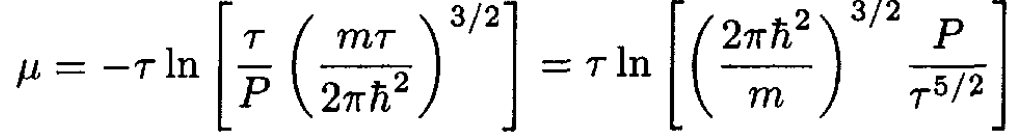 (4)
(4)
Now, consider an adsorption site: we can apply a Gibbs distribution with a variable number of particles to this site:
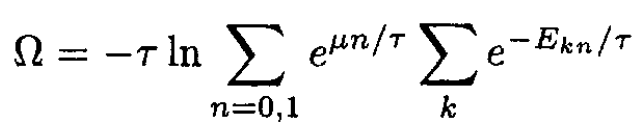 (5)
(5)
where the possible occupational numbers of the site for a submonolayer n = 0,1 (site is empty, site is occupied), with energy E0n = -nε0. Performing the sums, we have
 (6)
(6)
The average number of particles per site ⟨n⟩ may be written
 (7)
(7)
The total number of adsorbed particles N is given by
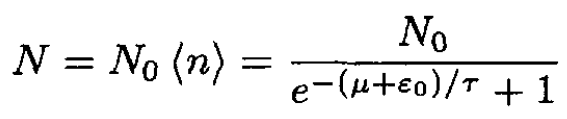 (8)
(8)
The surface concentration θ is simply
 (9)
(9)
Substituting μ for an ideal gas from (4) into (9), we have
 (10)
(10)
and
 (11)
(11)
where
 (12)
(12)
(9) can also be derived by considering the canonical ensemble. The number of possible ways of distributing N atoms among N0 sites is
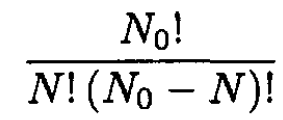
The partition function is then
 (13)
(13)
and the average number of particles
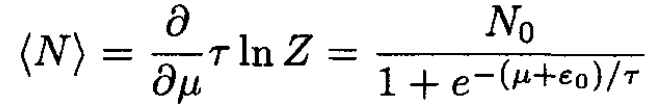 (14)
(14)
the same as (8).
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


