
Liquid-Solid-Liquid
 المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
المؤلف:
Sidney B. Cahn, Gerald D. Mahan And Boris E. Nadgorny
 المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
المصدر:
A GUIDE TO PHYSICS PROBLEMS
 الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 9
الجزء والصفحة:
part 2 , p 9
 30-8-2016
30-8-2016
 1597
1597
Liquid-Solid-Liquid
A small amount of water of mass m = 50 g in a container at temperature T = 273 K is placed inside a vacuum chamber which is evacuated rapidly. As a result, part of the water freezes and becomes ice and the rest becomes vapor.
a) What amount of water initially transforms into ice? The latent heat of fusion (ice/water) qi = 80 cal/g, and the latent heat of vaporization (water/vapor) qv = 600 cal/g.
b) A piece of heated metal alloy of mass M = 325 g and original volume V = 48 cm3 is placed inside the calorimeter together with the ice obtained as a result of the experiment in (a). The density of metal at T = 273 K is ρ0 = 6.8 g/cm3. The thermal capacity is C = 0.12 cal/g K, and the coefficient of linear expansion α = 1.1 × 10-5 K-1. How much ice will have melted when equilibrium is reached?
SOLUTION
a) Since the evaporation is very rapid, the heat to vaporize can only be obtained from the heat of fusion. Therefore, if mi of water becomes solid and mv vaporizes, we may write
 (1)
(1)
Since the total mass m = mi + mv, we have
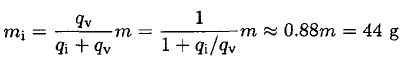 (2)
(2)
If we continue pumping, the ice would, of course, gradually sublimate, but this process takes much longer, so we can neglect it.
b) The metal cools from its initial temperature by transferring heat qm to melt some ice:
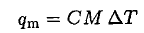 (3)
(3)
where ∆T is the temperature change. This may be determined from the sample’s density before it was placed in the calorimeter. Using the thermal coefficient of volume expansion β, where β = 3α, we have
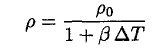 (4)
(4)
The temperature difference ∆T may be found from (4)
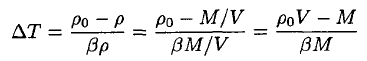 (5)
(5)
Equating the amount of heat required to melt a mass 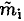 of ice with the heat available in the metal, we have
of ice with the heat available in the metal, we have
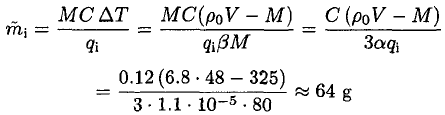 (6)
(6)
This mass exceeds the amount of ice from part (a), so all of it would melt.
 الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
الاكثر قراءة في مواضيع اخرى
 اخر الاخبار
اخر الاخبار
اخبار العتبة العباسية المقدسة


