


 الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
الفيزياء الكلاسيكية
 الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
الكهربائية والمغناطيسية
 علم البصريات
علم البصريات
 الفيزياء الحديثة
الفيزياء الحديثة
 النظرية النسبية
النظرية النسبية
 الفيزياء النووية
الفيزياء النووية
 فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
فيزياء الحالة الصلبة
 الليزر
الليزر
 علم الفلك
علم الفلك
 المجموعة الشمسية
المجموعة الشمسية
 الطاقة البديلة
الطاقة البديلة
 الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
الفيزياء والعلوم الأخرى
 مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء
مواضيع عامة في الفيزياء|
Read More
Date: 28-7-2016
Date: 11-8-2016
Date: 29-8-2016
|
Thermal Expansion and Heat Capacity
a) Find the temperature dependence of the thermal expansion coefficient if the interaction between atoms is described by a potential
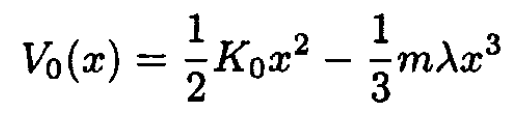
where λ is a small parameter.
b) Derive the anharmonic corrections to the Dulong–Petit law for a potential
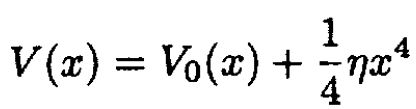
where η is a small parameter.
SOLUTION
a) First solution: We can calculate the average displacement of an oscillator:
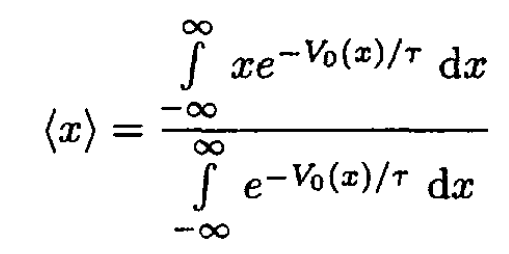 (1)
(1)
Since the anharmonic term is small, mλx3/3 << τ, we can expand the exponent in the integral:
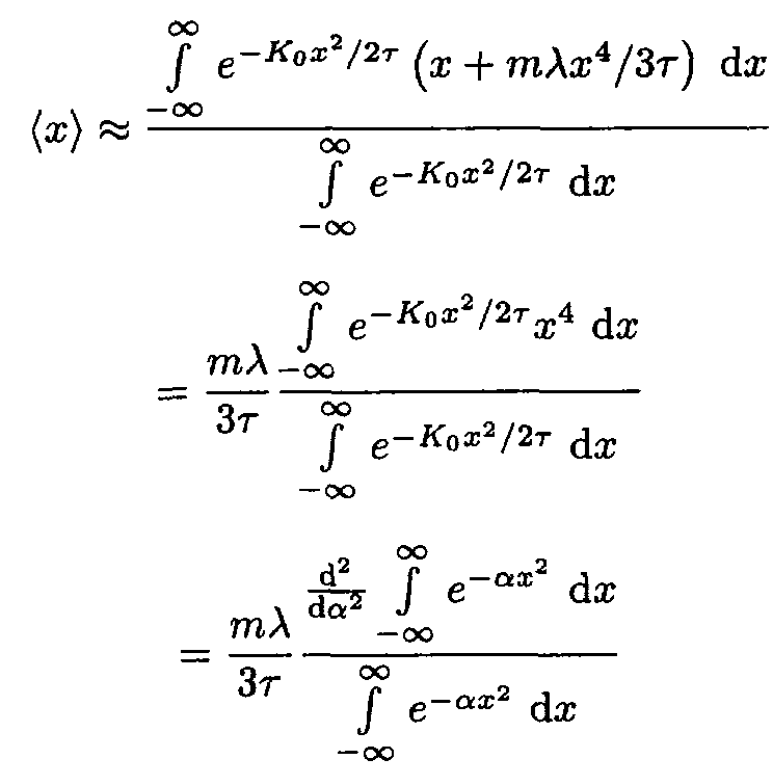 (2)
(2)
where we set α ≡ K0/2τ. So,
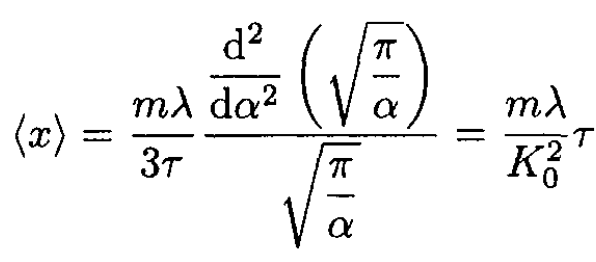 (3)
(3)
Note that, in this approximation, the next term in the potential would not have introduced any additional shift (only antisymmetric terms do).
would not have introduced any additional shift (only antisymmetric terms do).
Second solution: We can solve the equation of motion for the nonlinear harmonic oscillator corresponding to the potential V0(x):
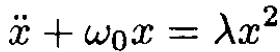 (4)
(4)
where 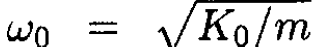 is the principal frequency. The solution gives
is the principal frequency. The solution gives
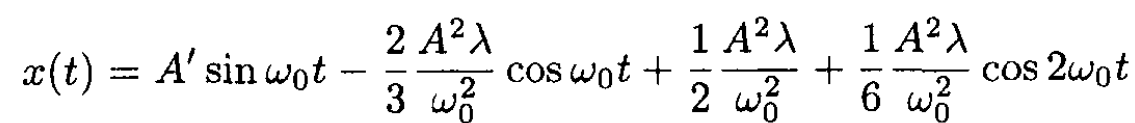 (5)
(5)
where A' is defined from the initial conditions and A is the amplitude of oscillations of the linear equation. The average ⟨x⟩ over a period T = 2π/ω0 is
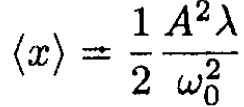 (6)
(6)
We need to calculate the thermodynamic average of ⟨x⟩:
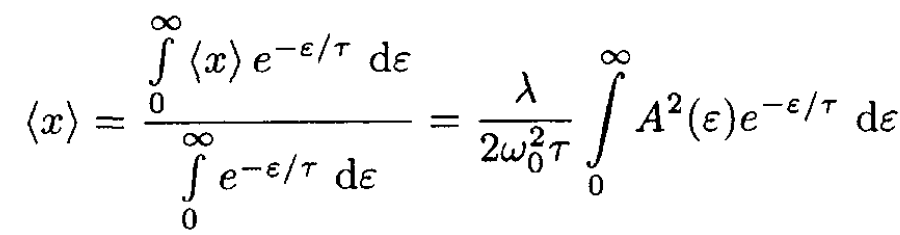 (7)
(7)
Substituting A2(ε) =2ε/K0, we obtain
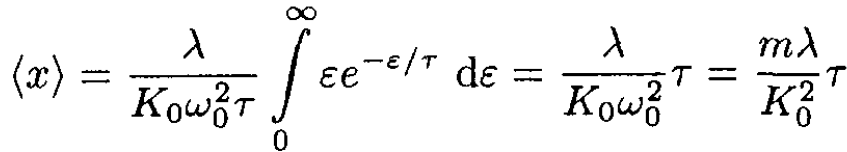 (8)
(8)
the same as before.
b) The partition function of a single oscillator associated with this potential energy is
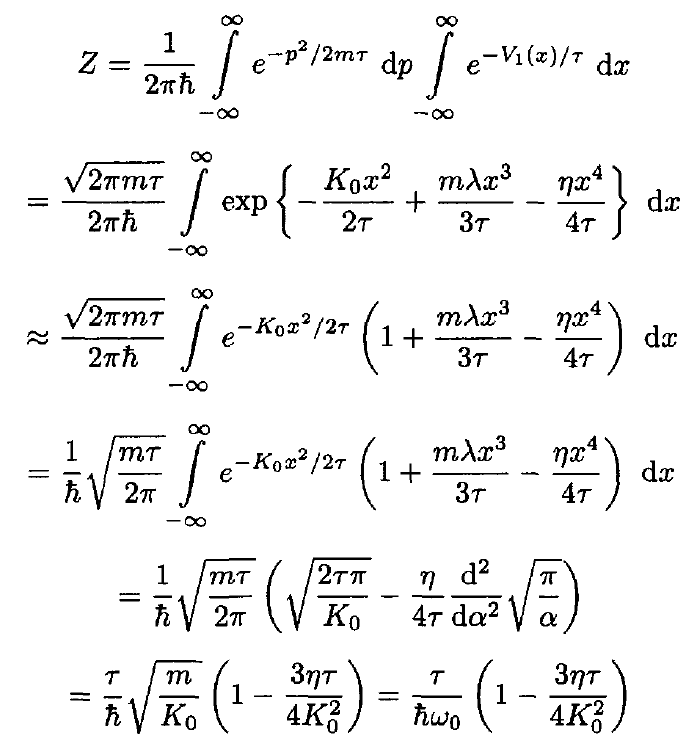 (9)
(9)
So, the free energy F per oscillator is given by
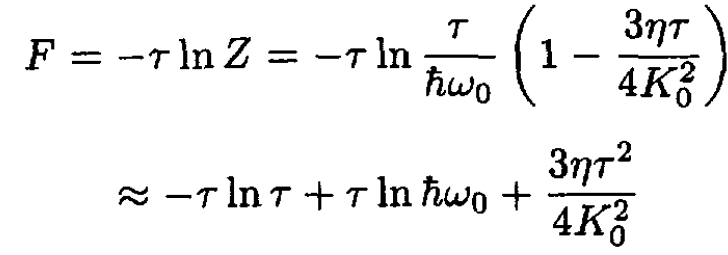 (10)
(10)
where we approximated ln (1 – x) ≈ - x. The energy per oscillator may be found from
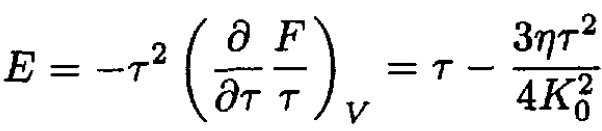 (11)
(11)
The heat capacity is then
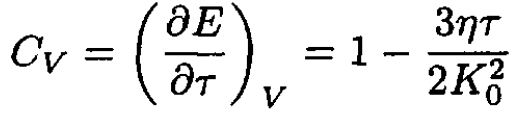 (12)
(12)
The anharmonic correction to the heat capacity is negative.



|
|
|
|
التوتر والسرطان.. علماء يحذرون من "صلة خطيرة"
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
مرآة السيارة: مدى دقة عكسها للصورة الصحيحة
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
نحو شراكة وطنية متكاملة.. الأمين العام للعتبة الحسينية يبحث مع وكيل وزارة الخارجية آفاق التعاون المؤسسي
|
|
|